The structure consists of several metal parts (screws, hooks, arches and springs). It is made individually for each patient. It is manufactured as follows: the orthodontist takes an impression of the jaw, a plaster model is cast in the laboratory, on the basis of which the plate is made. The orthodontist adjusts the position of the springs and hooks. This allows the doctor to move the teeth and rows of teeth in the right direction.

- Distal bite: correction and treatment in children and adults
- Causes of distal bite
- Periods of occlusion formation
- Ways to correct occlusion in children
- Age of bite correction in children
- LM activators
- Bite correction caps for children
- Alternative methods
- bite devices
- Myotherapy
- surgery
- How is strabismus treated in a child?
- Correcting squint in children – why is it so important?
Distal bite: correction and treatment in children and adults
Distal bite or prognathism is a condition in which the upper jaw is noticeably directed forward. Normally, when the jaws close, all of the teeth come into contact with each other. However, this is not the case if the bite is abnormal. Some teeth have no contact points or the contact points are displaced.
Causes of distal bite
The alignment of the jaws is determined during fetal development. If a woman has undergone a serious illness during pregnancy, it is possible that the process of jaw formation is disrupted and the bite is impaired. However, these disorders usually only appear after the birth of the child.
- Artificial nutrition. All babies are born with an underdeveloped lower jaw that faces backwards. The baby constantly tenses the jaw while sucking, and by 6 months of age the lower jaw has reached its normal position. The jaw remains retracted during breastfeeding.
- Bad habits. Sucking on a finger, a blanket, or the lower lip can cause the upper jaw to move backwards.
- Nasal breathing disorders. Incorrect breathing causes the mouth to constantly tilt. The tongue is in an awkward position and does not exert pressure on the upper jaw. The upper jaw narrows and the front teeth protrude.
- General diseases. Arthritis, endocrine disorders affect the growth of the entire body, including the jaw.
- Early tooth loss. Missing teeth mean that the lower jaw does not receive sufficient stimulation when chewing and its development is delayed.
- Injuries and inflammation. Fractures or osteitis (inflammation of the bone membrane) also delay the normal development of the jaw. Distal bite rarely occurs alone, but usually in combination with other anomalies.
Periods of occlusion formation
- First period: the period of newborns. During this time, infants do not yet have teeth.
- Second period: the teething period. It begins when the first baby tooth appears and continues until all 20 teeth have erupted.
- Third period: the period of changing teeth. It begins when baby teeth become permanent teeth.
- Fourth and final period: the permanent dentition. During this period, all molars should be in the mouth.
- inherited predisposition;
- dental defects;
- Early extraction of milk teeth;
- Teeth eruption later than planned;
- ENT diseases;
- gum disease;
- Constant consumption of liquid (soft) foods;
- Sores in the mouth;
- Prolonged sucking on the pacifier;
- Bad habit: finger sucking.
Ways to correct occlusion in children
A child's bite can be corrected in several ways:
1. Myotherapy. This method can be used to correct a child's bite without braces. This method involves performing special exercises that perfectly train the chewing and facial muscles. This method is very popular in the treatment of small children (from four years old). When prescribing and using this method of treatment, it is very important that the child understands why and how to perform the exercises correctly. An adult should be present to supervise the exercises. Attention should also be paid to the regularity of the exercises.
2. Devices. This method uses special structures (equipment, trainers, plates). These devices can be used from the age of 6.
3. surgical. This method involves surgical intervention on the jaw.
4. orthopedic. The bite is corrected using orthopedic constructions (veneers).
5. comprehensive. Consists of several methods.
Age of bite correction in children
A visit to the orthodontist should be considered if baby teeth have erupted. If necessary, the specialist will recommend a comprehensive examination and x-rays to diagnose the causes of the dental abnormalities. Subsequently, it is advisable to consult specialists in related fields. Specialists will identify contraindications, the likelihood of complications, and assess the condition of the child's entire body. Based on the results of the examination, the orthodontist creates a treatment plan for approximately two years with monthly visits to the clinic.
In modern dentistry, there are various types of devices for correcting dental misalignments in children, designed to achieve the following goals:
- prevention of bad habits;
- expansion of the maxillary arch;
- correction of speech errors;
- normalization of chewing muscles;
- Control of tongue position.
LM activators
These orthodontic devices stimulate the development of the jaw arch, chewing muscles, facial expressions and proper breathing. They are also suitable for changing bad habits such as sucking fingers, biting lips, chewing pencils or nails. By acting on the gums and tongue, the child's buds are fixed in the correct position and prevent the development of jaw abnormalities in the future.
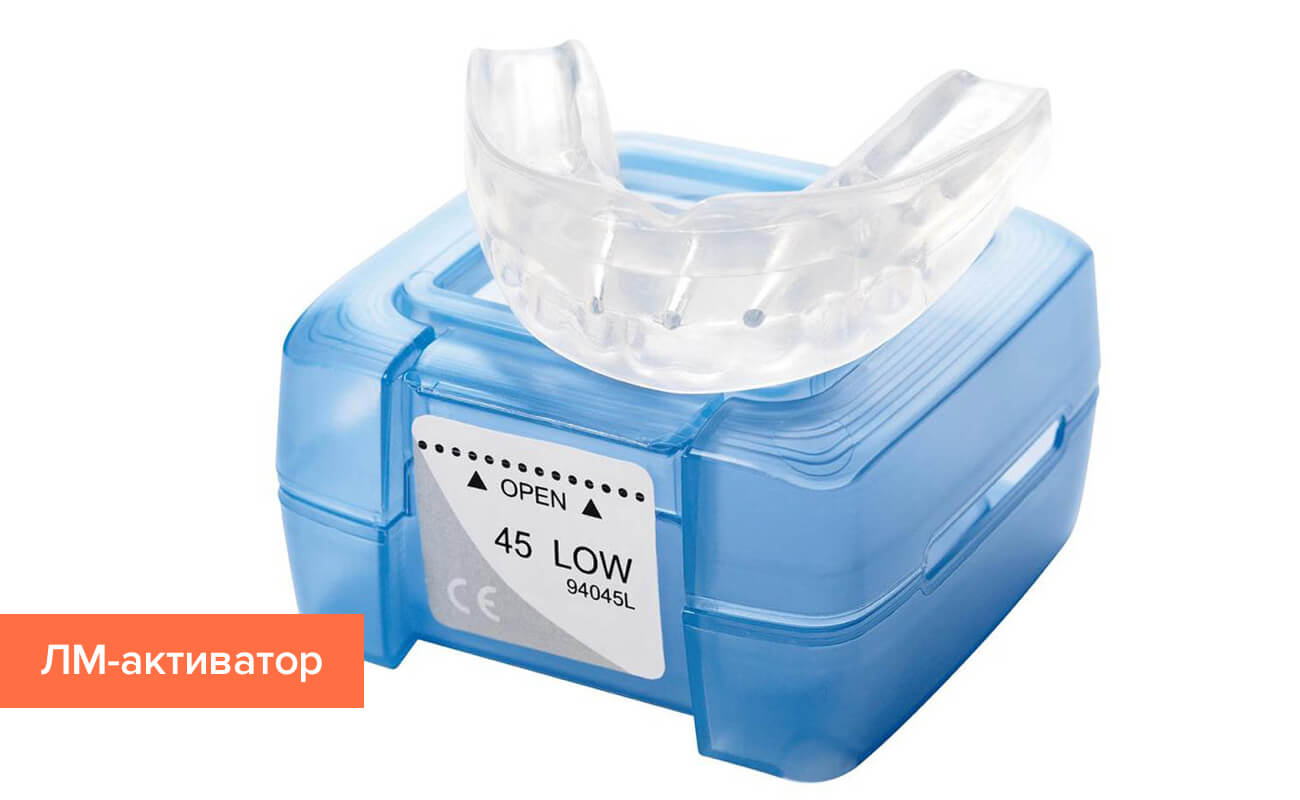

Bite correction caps for children
Correcting a child's bite at 3 years old requires minimal investment. At this age, the teeth are still very malleable and treatment is usually limited to the use of a bite guard. It is only worn at night to align baby teeth and avoid later problems when they are replaced by molars. The overlay is a band made of rubber strips that is attached to the jaw. Braces are also used to correct mesial occlusion, which means stopping the development of the lower jaw so that the upper jaw can form properly.
Alternative methods
bite devices
As an alternative to braces, the orthodontist may suggest bite splints to correct the bite for children aged 17 to 18 years. They can be used to correct deformities of the upper and lower jaw in children.
Myotherapy
Another alternative for bite correction in children is myotherapy. This technique involves correcting the child's bite through special exercises. With regular exercises, the muscular system begins to work properly and the teeth become aligned. The special thing about this method is that it can be used both as a sole or as an additional means of correcting dental defects. It is suitable for children up to the age of four, so no adult supervision is required during the exercises.
However, myoma therapy is not suitable for every child because there are the following contraindications
- Impairment of the mobility of the jaw arch;
- hypertrophy of the muscle;
- Severe dental arch abnormalities;
- Deformity of the temporomandibular joint following illness or trauma.
surgery
Surgical procedures are also a method of correcting bites without braces in older children, but they are not common and are only used as a last resort. Surgical correction of bite misalignments in children under 12 is usually only performed for certain indications. These include the following defects:
- Congenital malformations of the jaw;
- asymmetry of the face;
- dysplasia of the chin;
- Skeletal abnormalities;
- Deformations of the cranial vault.
In all other cases, the specialist will try to solve the problem in a less drastic way, for example with braces or dentures.
How is strabismus treated in a child?
For the proper training of the eyes and the development of the eye muscles, parents should do gymnastics with their child:

- Sit the child on your lap and show him a large, bright toy that he can move in different directions.
- Turn on a table lamp and attach a colored ball with a diameter of 1 cm to it. Cover one of the child's eyes with your hand. Move the lamp with the ball from side to side and hold it in different places for 20-30 seconds.
- Hang rattles above the crib that the baby can reach with his hands.
- Vary the placement of toys above your baby. He may like one of them and look at it all the time, which is not good for the proper training of the eyeballs.
All of these preventative measures help the newborn learn synchronous eye movements more quickly. Gymnastics should be approved by the doctor. He or she will also recommend other specific exercises. There may be contraindications for these. The eye exercises should not be performed if the baby feels unwell. They should also not be carried out for long periods of time. The child must not get tired. However, gymnastics is only effective if it is done daily.
According to some doctors, the baby's eye movements are not synchronized and this is a natural condition. At the beginning the eyes only move horizontally and later vertically. Therefore, you shouldn't worry too much if the baby blinks a little in the first few months of life. However, all parents should take care to prevent squinting. Because it can later lead to serious eye defects.
Correcting squint in children – why is it so important?

Strabismus can have serious consequences if left untreated. Squinting can lead to loss of vision in both eyes. One eye may fall completely out of sight. This can lead to difficulties in one profession or another. A squint is also a cosmetic defect. Many people find this embarrassing. At school, the child can become an object of ridicule. Today there are a wide range of options to avoid the complications of strabismus. A holistic approach should be taken when treating and preventing strabismus.
Read more:- What is distal?.
- Podiatrist what kind of doctor.
- How to treat clubfoot in a child.
- Who is the orthopedist?.
- A child begins to have clubfoot between the ages of 1 and 5.
- What is an orthopedist?.
- What does an orthopedist examine?.
- How to cure a clubfoot.
