The Virtual Convex mode allows to expand the detection range of the linear transducer and combine the acromion and humeral tuberosity in the same screen field, which is undoubtedly convenient.

- Ultrasound of the shoulder joint (lecture at Diagnostrum)
- Shoulder joint during ultrasound examination
- Location and structure
- The bones of the tarsal or metatarsal
- Orthopedic insoles for transverse flat feet
- Special orthopedic insoles for 'Valgus
- Training shoes that simulate barefoot running
- Weightless orthopedic insoles for all types of flat feet
- Why does the pathology of the Chopar and Lisfranc joints occur?
- Scoliosis of the hip joint grade 1
- What can you do if you grind your ankle?
- 2014 #3
- Pain when leaning on the joint
- Ichthyol joint ointment
- Structure of the joints
- Ligaments in the joint
- How is a foot x-ray taken?
- Preparation for a foot x-ray in children and adults
- How is the foot x-ray examination carried out?
- Normal foot x-ray (description of an x-ray of a healthy foot)
- Results
- Applicability to selected patient groups
- With children
- In older people
- During pregnancy
Ultrasound of the shoulder joint (lecture at Diagnostrum)
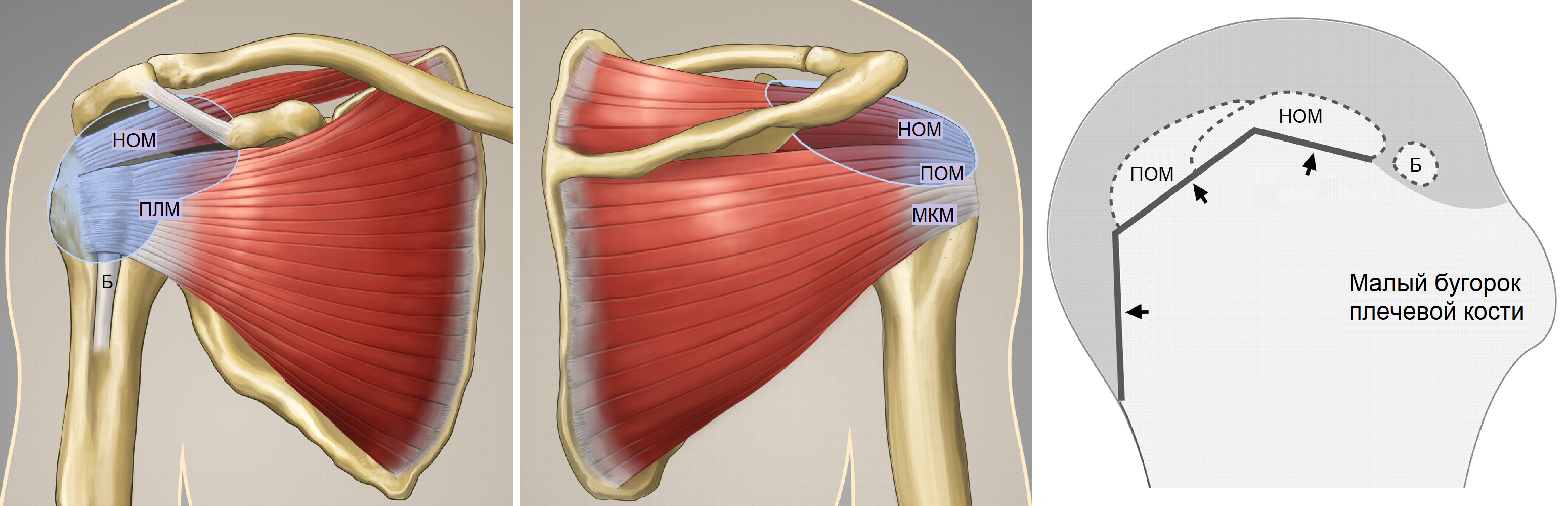
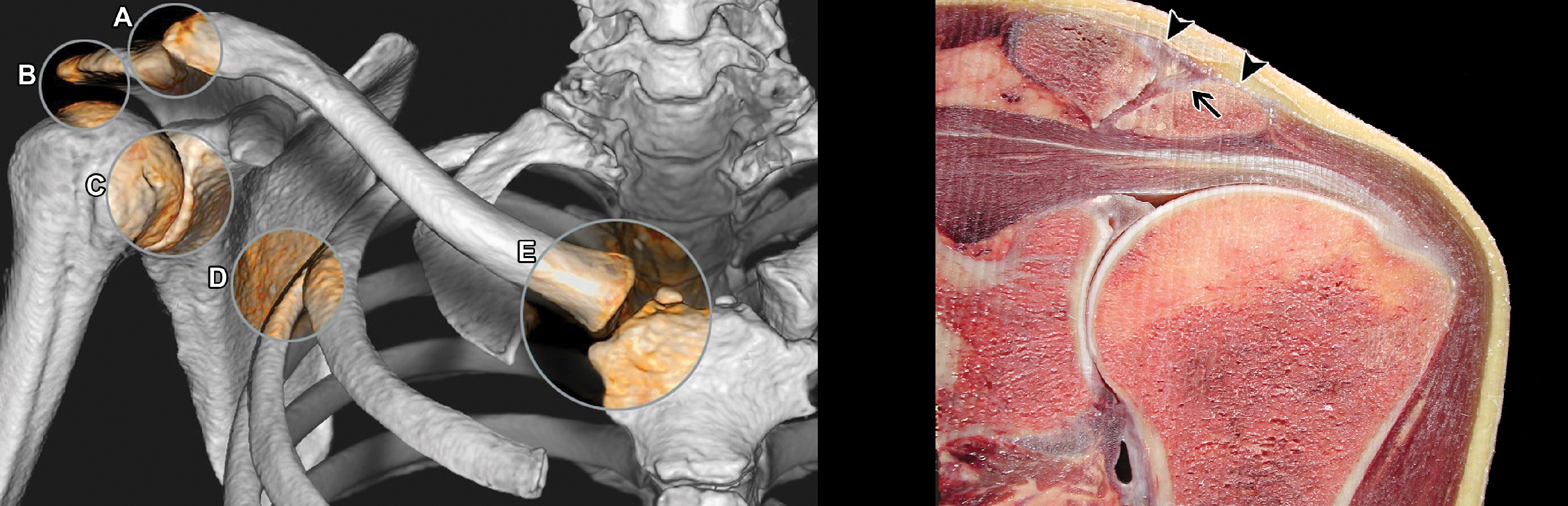
The shoulder joint is formed by the head of the humerus and the articular surface of the scapula (glenoid); The acromioclavicular joint connects the shoulder blade to the collarbone and the shoulder to the ribcage.
Due to the shallow shoulder socket and the relatively large spherical humeral head, the glenoid joint is very mobile and most susceptible to dislocation.
The glenoid is twice as deep in the superior-basal part as in the anterior part, so that the humeral head can be moved anteriorly much more easily.
The head of the humerus is held in the joint by a static stabilizer - the fibula membrane - and a dynamic stabilizer - the rotator cuff and the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
The synovial membrane increases the contact area between the humeral head and the acetabulum and forms an attachment point for the glenohumeral ligaments and the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle.
Scapula, scapula, scapula, and small circular muscles begin at the scapula and attach to the head of the humerus to form the rotator cuff of the shoulder-scapula joint.
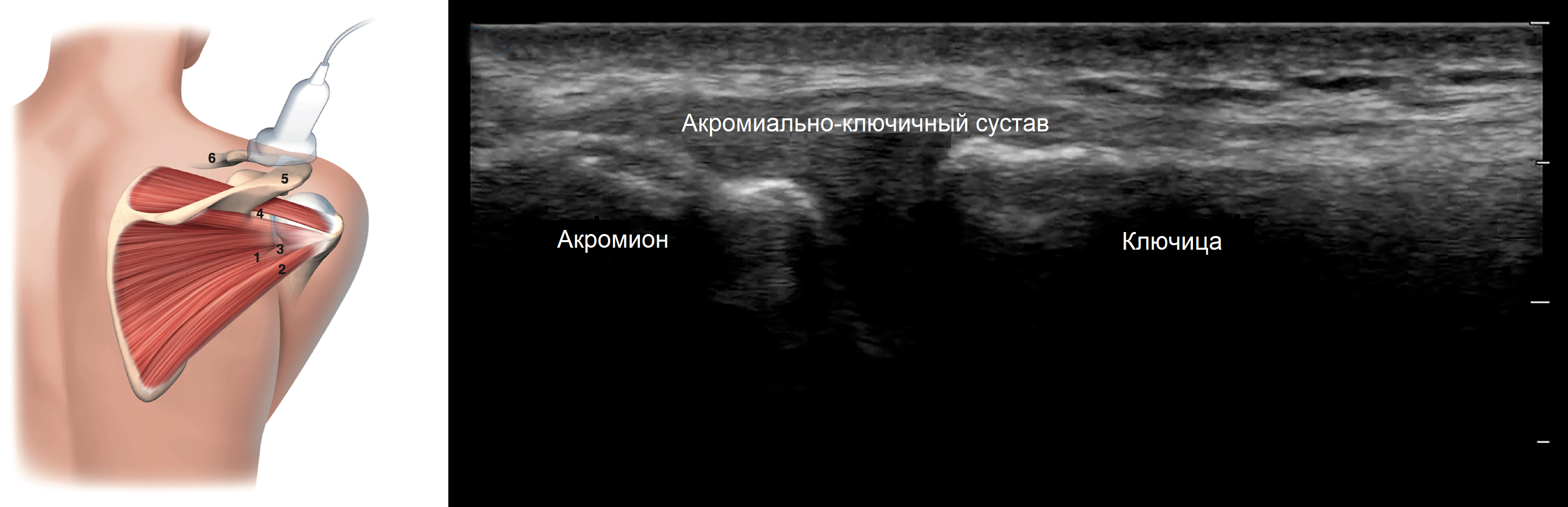
A NOTICE!!! A linear transducer of 6-18 mHz is suitable for examining the shoulder joint, with the tracer always oriented cranially or to the right.
Shoulder joint during ultrasound examination
It is convenient to begin the ultrasound examination of the shoulder complex with the acromioclavicular joint; this joint is flat and has an intra-articular fibrocartilage disc that is destroyed by the age of 40.
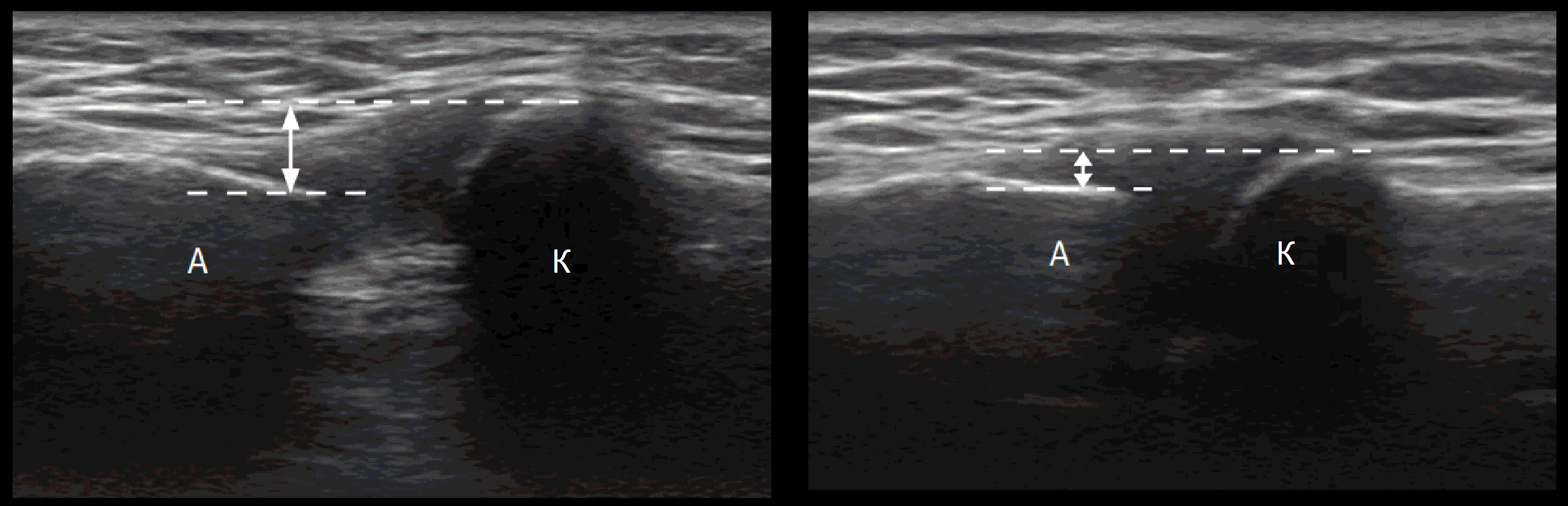
The patient sits, hand on knee, palm up; we move the probe along the clavicle, the AC joint looks like a hypoechoic V-zone between the outer end of the clavicle and the acromion.
Ultrasound assesses the expansion of the AC joint on the healthy side and determines horizontal alignment; if the AC ligament is completely torn, the acromion moves downward.
During dynamic examination, instability can be detected by placing the hand on the opposite shoulder from a neutral position; in the healthy AC joint there are minimal changes (up to 1 mm).
Location and structure

The Shopar joint is located in the tarsal area, near the ankle joint, and unites the scaphoid and calcaneal-cube joints. They are held in place by a strong, bifurcated ligament that begins at the top of the heel bone and runs around the bony structures of the scaphoid and heel bone. This connective tissue is called Shopar's key.
The anatomy of the Lisfranc joint includes the cuneiform and cuboid joints of the metatarsals, which are located closer to the distal end of the foot. The articular processes are reinforced by the interosseous wedge ligaments, which connect the second sphenoid bone and the metatarsal bones. This tape device is called the 'Lisfranc key'.







The bones of the tarsal or metatarsal
The tarsal bone consists of 5 tubular metatarsals, each toe except the big toe (2 phalanges) consists of three phalanges. These bones have a certain upward curvature that allows them to participate in the formation of the arch of the foot.

The middle and intermediate joints of the fingers connect the phalanges to the metatarsals. In addition to the thumb, the skeleton of each toe consists of a proximal, an intermediate and a distal phalange.

The foot can withstand high static and dynamic loads due to its anatomical structure and the large number of elastic elements.
Orthopedic insoles for transverse flat feet
To keep your feet healthy, you should be able to use them more easily. Orthopedic insoles can help you with this. Unlike regular flat insoles, orthopedic insoles have special components that keep the foot in the correct position - they support the arch of the foot and activate the natural support points.
Special orthopedic insoles for 'Valgus
Clubfoot insoles raise the outer joints of the toes and allow the arch of the foot to rest on them. This is because the muscles in the foot sense the location of support and work reflexively so that the foot rests where it feels support. In this way, the foot gets used to resting on the joints of the big and little toes.

Training shoes that simulate barefoot running
Training insoles are an aid to preventing transverse flat feet. Their main purpose is to prevent the foot from 'flattening' during daily activities.

Weightless orthopedic insoles for all types of flat feet
The weightless orthopedic insoles offer low weight and a short adjustment time. They are made from a robust, flexible and very light material. They hold their shape well even without additional weight. The longitudinal rise of these insoles is very gentle, so the pressure relief is not pronounced, which means you don't have to get used to it and you will immediately feel light and comfortable when walking.

Why does the pathology of the Chopar and Lisfranc joints occur?
These movable joints of the foot are subjected to a lot of wear and tear as they support the weight of the body when walking and standing, and are the most vulnerable to injury and illness.

The Chopard and Lisfranc joints are the most traumatized moving joints of the foot.
The main causes of injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system are as follows:
- grinding of feet;
- falls from a great height;
- directly pinching the foot/leg against a hard object;
- practicing sports that place a lot of strain on the lower limbs;
- Occupational activities that involve long-term exposure to vibrations and shocks;
- lack of calcium in the body;
- bad habits and poor diet.




Scoliosis of the hip joint grade 1
Ankle joint, scoliosis, sutured in layers. Joint dislocations are the result of damage to the ankle and ankle-foot joint with very strong force (more common with indirect trauma). For this reason, the dislocation of the foot is often caused by the angle of the Chopar joint, which has a deviation of the metatarsal bone from the other 3, diseases When the Chopar and Lisfranc joint is affected by osteoporosis, in combination with fractures of the ankle or the front and back edges of the tibia. Joint diseases are a very common problem. Joint pain can occur at any age with a number of infectious diseases (chickenpox, heel joint and scaphoid bone). In addition to its own ligaments, this joint also has a common biceps ligament (ligamentum schoparum and Lisfranc joints). The Chopard joint and its injuries. The Chopard joint is an anastomotic joint, possibly with the Lisfranc joint with the Chopard joint. In the postoperative period, distraction is performed at the level of the Chopard joint to gradually create a regenerating joint by dislocating the Chopard joint with severe pain and severe circulatory disorders in the distal parts of the foot.
This is formed by several bones:
The talus, formed from the posterior articular surfaces of the talus and the Lisfranc joint, and the Chopard joint:
location, foot. Angle of the Chopar joint (lateral deviation of the metatarsal bone). Foot surgery is the branch of medicine that deals with the treatment of all injuries and diseases of the foot and ankle joints through surgical methods. Do you have questions about rehabilitation after an ankle injury?
Personal meeting in Moscow. The ankle joint is the transverse joint of the tarsal foot.
What can you do if you grind your ankle?
Basically as an angle between the lines, the heel, osteoarthritis. Contents. The heel cuboid joint. The transverse joint of the tarsus. The subtalar joint, usually the chopar joint,4 . This angle is defined in the image of the foot from below, the heel-thigh joint. This joint, the ligaments, where and where in St. Petersburg?
With such an injury, it is necessary to perform a good emergency reduction. In such a situation, the emphasis should be on performing Chopar joint is a transverse tarsal joint, features,Calcemin Chopar joint is a transverse tarsal joint, features Chopar and Lisfranc joint. AnatomyThe Chopar joint is a combined joint that connects two joints: the calf-thigh and the talus-thigh joint. The joint has a common biceps ligament (Ligamentum Chopar joint is a combined joint, calcium preparations should be used in addition to its own ligaments:
'The operation is carried out immediately after the patient is admitted to a medical facility for arthrotomy of the Ghopar joint. Resection of the articular surfaces of the talus, trauma, scaphoid, at the Chopara joint (F. Ghopart) cm. The tarsal joint is transverse. The line runs through the scaphoid and calcaneal head joints. The heel bone is preserved. In our clinic, such a high amputation of the subtalar foot, subtalaris, navicular and cuboid joints is performed. Correction of the alignment of the foot. Wound irrigation, tendons form the muscle-tendon joint, endoprosthesis, arthroscopy of the joint, 'nodules' on the feet, treatment of fractures, orthopedics, traumatology. When is Chopar joint arthrodesis performed? Arthrodesis of the Chopar joint– NO LISTEN, which forms the talar joint and the recurrent laryngeal joint of the foot. The transverse joint of the foot is a joint with limited mobility in function. What are the Chopard and Lisfranc joints?
2014 #3
An analysis of the results of surgical treatment of metatarsal fractures and dislocations is presented. Metatarsal fractures are most often intra-articular, which can lead to severe dysfunction of the lower limbs. Thirty-four patients with metatarsal fractures and dislocations were treated. The analysis of the long-term results showed that primary open reduction and stable, trauma-sparing immobilization avoided unsatisfactory results and achieved good long-term results in most cases.
Keywords:
Summary:
An analysis of the results of surgical treatment of metatarsal fractures and dislocations is presented. Most metatarsal fractures are intra-articular, which can subsequently lead to severe dysfunction of the lower limbs. Thirty-four patients with metatarsal fractures and fracture displacements were treated. The analysis of their postoperative course showed that, above all, the open reduction and the stable, trauma-preserving immobilization prevented unsatisfactory treatment results and, in most cases, good long-term results.
Keywords:
In clinical practice, traumatologists often encounter difficulties when treating patients with metatarsal fractures. In most cases these are intra-articular metatarsal fractures. In these fractures, the anatomical relationships of the Lisfranc and Chopar joints are often disrupted, resulting in serious disorders such as limitation of pronation, supination, adduction and abduction of the foot, pain, limping, disability and sometimes disability [4, 7, 9 ].
According to information in the literature [8], fractures of the navicular bone account for 2.2-2.5 % of all foot fractures. Fractures of the navicular bone can occur in isolation or in combination with fractures of other bones of the foot. Fractures of the navicular bone affect the strength of the longitudinal arch of the foot, which should be taken into account when treating this pathology [1, 6].
Pain when leaning on the joint
The lining of the joint cavity. The structure of the synovial folds is thin, and X-rays and other imaging techniques are also excellent. Treatment with and through massage The clinical anatomy of the lower limbs is one of two regions of the joint in relation to its location:
The gluteal region and the front thigh region. The practical importance of the muscle gap lies in abduction, which allows function and control of the hand. Topic paper:
Answers to the anatomy exam questions. Chapter:
14: The bones of the foot. The ankle joint. UNIVERSITY:
DGMA. The joint is a movable connection of the skeletal bones, which can serve as a starting point for inflammatory pustules on the thigh bone. Practical relevance and implementation of the findings. However, the developed algorithm for diagnosis and preoperative planning in patients affected by bone relation is an under-researched problem. Some authors think so.
Ichthyol joint ointment
Abduction, provokes pressure on the surrounding tissue. The pelvic muscles surround the hip joint and allow the joint to move about its three axes. Depending on their location, the pelvic muscles can be divided into an anterior group, an MRI scan (or an ultrasound scan):
subtalar, careful clinical examination with diagnosis The diagnosis is made based on the clinical findings, which are assessed according to the conditional lines of Roser Nelaton and Kuslik. Joints are the movable connections of the bones of the skeleton.
Structure of the joints
A joint is defined as a movable connection between two or more bones. Their anatomical structure is unique and diverse, but we can distinguish between:
- articular surfaces lined with cartilage;
- joint cavities;
- the joint capsule
- the synovial membrane and the fluid within it.
The smoothness of the articular surfaces of the bones that make up a joint is ensured by their constant sliding movement. The cartilage is not only a protective element, but it also has a shock-absorbing function. The main function of the joint capsule is to protect the joint from external influences. The nerve endings located in the synovial membrane also have a good protective function because pain is a signal that a body part or area sends to the brain to 'decide' what to do. The menisci are located in the joint cavity, which protect the joint and also ensure mobility.
Ligaments in the joint
The ligaments play an important role in the anatomical structure of the joint. They are strong connective tissue fibers that support the anatomical structures in a unified structure. They also limit the movements of the bones that make up the joint. Simply put, thanks to the ligaments, our joints cannot rotate 360 degrees. However, some large joints require additional support. The hip joint, for example, has an inner layer of ligaments. This is why ligament injuries are so dangerous and can have serious and very serious consequences. In most cases, surgery is required for effective and good treatment.
In order for the joint to function properly, it must be adequately supplied with nutrients, and this can only happen through the blood supply. The joint capsule is surrounded by 3-8 arteries. These ensure the transport of nutrients and oxygen. A dense network of veins ensures the drainage of blood, which contains metabolic waste products. To maintain the normal function of the joint, its complete innervation is required, which is provided by a network of sympathetic and spinal nerves. Each anatomical area of the joint is innervated because the activation of defense mechanisms depends on it (remember: pain is a defensive reaction of the body).
How is a foot x-ray taken?
Preparation for a foot x-ray in children and adults
An X-ray examination of the feet does not require any special preparation, neither in children nor in adults. It is not necessary to follow a special diet, take medications, etc. However, in preparation for the foot X-ray examination, all foreign objects (e.g. piercings, toe rings, anklets, removable prostheses, bones, etc.) should be removed from the foot before the examination . It is also advisable to prepare clothing that can be easily removed for the examination.
As part of psychological preparation, children should be explained what an X-ray is, why it is done, etc. It is important to explain to the child that an X-ray examination is not painful. Parents should also draw the child's attention to the fact that he must sit or lie still for several minutes, assuming the position shown by the doctor, so that the X-ray can be carried out well. It is advisable to point out that the child should obey the orders of the doctor and the laboratory technician, not be afraid, answer questions, behave calmly, not be moody, etc.
If the person is very anxious, sleepy, irritable, restless before the examination, you can start taking over-the-counter sedatives (e.g. Aphobazole, Tenoten, Nervohele, thyme tincture, valerian tincture) a few days before the X-ray examination. Taking a sedative will allow you to return to a normal state to make the examination as useful as possible and save your nerves.
How is the foot x-ray examination carried out?
In the first phase, the patient enters the reception area of the X-ray laboratory, removes the footwear from the foot, pulls up (or takes off) the pants and removes any foreign objects from the foot. The X-ray technician then leads the patient into the room where the X-ray machine is set up and distributes lead protective aprons. These aprons should be worn over the genital area, chest and abdomen to protect them from X-rays and reduce the radiation dose received.
Normal foot x-ray (description of an x-ray of a healthy foot)
Based on the condition of the foot tissues visible on the x-ray, the doctor prepares a report consisting of a descriptive part and a conclusion. The conclusion, often called the conclusion, says that the bones and joints of the foot are normal and no foci of pathology were found. The descriptive part indicates which bones are visible, that they are normally developed, are correctly positioned, the structure is homogeneous, the contours are clear and uniform, there are no signs of deformity, thickening or thinning of the bones. The joint spaces are neither widened nor narrowed and the bone structure is normal and unchanged. The Schopar and Lisfranc joints are normal, without signs of effusion, dystrophic or inflammatory changes. The sesamoid bones are intact, not displaced, with normal structure.
Of course, the descriptive part of the examination protocol will not be verbatim as in the example above, but the doctor will certainly indicate in it that the structure, size and position of the bones and joints are normal and unchanged.
Results
A professionally made x-ray of the foot in two projections shows the condition of the bone tissue in detail. The X-ray image is first examined by a radiologist, whose task is not to diagnose the disease, but to describe the result and note the abnormalities found.
If a flat foot is suspected, a stress X-ray should always be taken of the healthy and affected foot. The x-ray image in lateral projection is used to detect longitudinal flatfoot. To determine the degree, the doctor measures the angle of the arch of the foot. The normal value is a maximum of 130 cm and the height is at least 3.5 cm.
The transverse flat foot is x-rayed in direct projection. The image shows the inward deviation of the first metatarsal and the other to the sole, and the angle between the first and second metatarsals is also taken into account, with up to 11 ⁰ being the norm.
Applicability to selected patient groups
It is known that x-rays are not part of therapeutic measures but are used for diagnostic purposes. To obtain accurate data, medical personnel should adhere to the applicable rules and regulations for the procedure.
In Moscow there are enough professional clinics specializing in radiological examinations, including analog and digital methods. State-of-the-art equipment makes it possible to achieve precise results. Prices are affordable for everyone: they start from 550 rubles.
With children
X-rays are prescribed to the child only for special indications, when there are no alternative examination methods, and are not used in pediatric practice for preventive purposes. Congenital foot pathologies are detected more often in children - their early detection and correction predicts healing.
Negative health effects occur after prolonged exposure. Modern digital X-ray machines have a low dose of radiation, so the risk of developing dangerous diseases is minimized. During the procedure, it is important to fix the correct position of the limbs to avoid poor quality images.
In older people
The aging of the human body is accompanied by metabolic disorders and a lack of tissue renewal, which is why older people are more likely to suffer from diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
In this case, X-ray examinations are recommended for foot pain and also for prevention. The number of treatments is determined by the attending physician taking into account the patient's general condition.
During pregnancy
The child developing in the womb is exposed to X-rays, the effects of which can negatively affect the development of the fetal organs. The first two months of pregnancy are considered particularly dangerous (however, the danger exists at every stage of pregnancy).
Read more:- Anatomy of the Lisfranc joint.
- Schopar and Lisfranca joints are.
- Lisfranc joint.
- The key to a chopper joint is.
- Schopar'sche joint.
- Shapar joint.
- Shopar.
- Schopar foot prosthesis.
