Symptoms include a grinding sound, pain, characteristic stiffness, and swelling.
- Bone tumors in children: where do the chondromas come from and what are they?
- What is a chondroma?
- Care at the highest level: what modern diapers can do
- Nodules in children and adolescents
- Treatment
- What is the risk of a mass occurring?
- Which doctor should I see?
- causes
- complications of the disease
- diagnostic measures.
- Causes of synovitis
- classification
- Other effects of bursitis?
- What to do if a bump appears on the foot?
- video overview
- symptoms
- causes
- How the disease is diagnosed
- Primary Treatment Methods
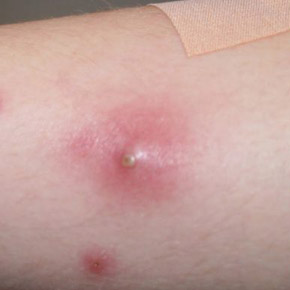
Bone tumors in children: where do the chondromas come from and what are they?

Benign bone tumors are a common problem in childhood and adolescence. Although the diagnosis used to be considered an indication for cancer removal, recently researchers have found that the number of bone tumors in children is underestimated and, on the contrary, the risk is overestimated. MedAboutMe explains what these bone growths are and how to treat them.
What is a chondroma?
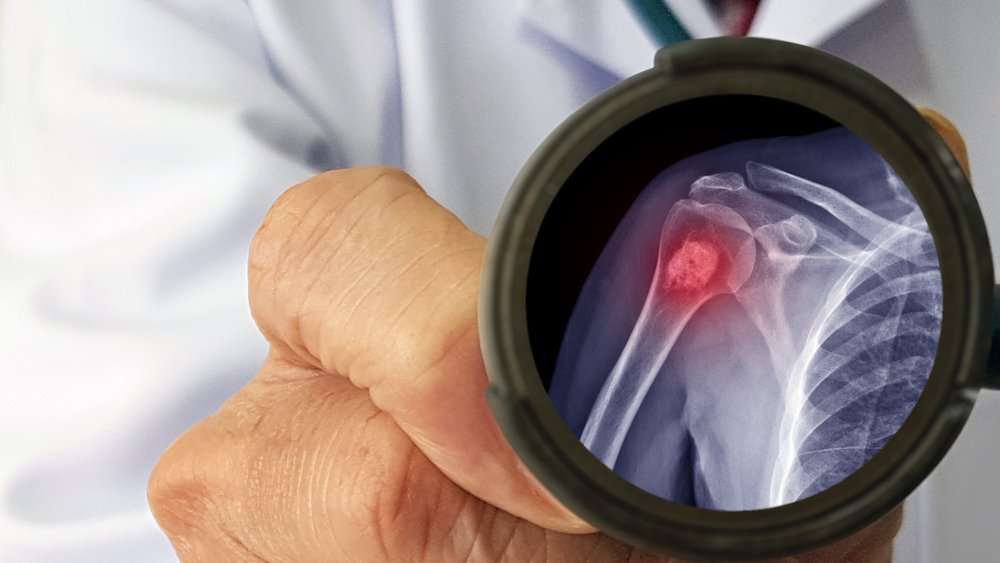
The most common diagnostic finding in pathological bone tumors in childhood are chondromas, benign tumors that grow very slowly. Symptoms do not appear immediately, and the rate of growth depends on the location. In contrast, the most common bone tumors in children are commonly referred to as fibroids and are considered relatively safe variants of the age-related norm.
As a rule, the first symptoms of a tumor do not appear until it is large enough to press on adjacent anatomical structures.
Chondromes account for 12 % of all skeletal tumors and are called juvenile bone tumors because of the age of the patients: the peak of discovery is in puberty.
The exact causes of chondromas are not known, but there are a few theories. Scientists have established that a tumor can form:
A distinction is made between internal and external chondromas—those that grow inside the bone and deform it, and those that form on the surface of the bone tissue.
Chondromes most often occur on carpal bone structures, less often on long bones.
Although chondromas are benign, they can develop into osteosarcoma, a dangerous type of cancer. This happens most often when the tumor is on the scaphoid or sternum.
Tubular chondroma degeneration is so rare that it is classified as a medical error.

Care at the highest level: what modern diapers can do
Nodules in children and adolescents
In children and adolescents, nodules usually develop after an injury to the knee or after heavy physical exertion during sports training.
Lumps can appear in these areas:
Sports that can injure knees and cause nodules include active team games. Exercises that hurt the knees with heavy use:
- roller skating or ice skating;
- jumping (especially high jumping);
- running (for speed);
- Gymnastics;
- Team games (football, volleyball).
Most commonly, lumps appear during puberty in adolescents. In addition to the injury, the child may also have pre-existing medical conditions:
The appearance of a node should not be left untreated, as it can lead to the development of other pathologies and complications. Depending on the disease, different complications can occur.
Treatment

Treatment depends on the underlying cause. The doctor diagnoses the disease, conducts all the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribes the appropriate treatment.
For joint disease, treatment consists of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are the most commonly used drugs:
These drugs reduce the inflammation, which in this case is the cause of the nodule formation. The nodule formation will subside along with the inflammation.
How does a child develop a rash on the elbow? Find out here.
If there is a cartilage lesion, medications are prescribed to repair the cartilage. The medication (tablets) must be taken over a long period of time because the cartilage takes a long time to regenerate. The medication can help with minor damage to the tissue.
For diseases that affect the bones of the knee joint, regenerative drugs and vitamins (calcium, phosphorus and others) are prescribed. Medications are ineffective for large lesions.
Treatment is comprehensive and usually conservative (in very rare cases, surgery is recommended). Treatment may include exercise and wearing special shoes.
What is the risk of a mass occurring?

A Baker's cyst is a benign condition that does not develop into a malignant tumor. However, if it causes discomfort over a long period of time and does not appear to be reducing, its removal should be considered.

Mechanical trauma or excessive exercise can cause the cyst to rupture, which is associated with severe swelling and pain.
In rarer cases, the cyst presses on the veins of the lower limbs, leading to an inflammatory process called phlebitis. This creates the conditions for the formation of blood clots in the deep vessels of the lower limbs.
However, such complications are more common in immunocompromised people suffering from multiple chronic diseases. Small cysts can even go away without surgery, a study by researchers has found.

In 2013, experts from Chiba Children's Hospital in Japan published a paper examining the health status of children with cervical tendon cysts.
They found that the cyst in 85 % of the young patients shrank naturally within a year of diagnosis.
Which doctor should I see?
If symptoms are suspicious, a pediatrician should be consulted. The doctor examines the child, collects the symptoms and medical history, and then refers the child and parents to a surgeon for evaluation and advice.

Which study is the most insightful?
In 2011, German researchers from the Institute of Radiology in Würzburg published a study on the diagnosis of a popliteal cyst. Specialists examined the children using various methods: ultrasound, MRI or CT.
It turned out that the ultrasound had the highest sensitivity. Unlike other diagnostic methods, ultrasound could detect even small masses.
causes
The actual cause of the development of fibroids in children has not yet been clarified. Specialists have identified a number of factors that contribute to the formation of tumors. This includes:
- Unfavorable living conditions in the environment (proximity to chemical and cement plants, landfills, contaminated areas);
- Frequent injuries, bruises and falls;
- Various acute and chronic infectious diseases;
- Inappropriate use of strong drugs;
- endocrine disorders;
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
complications of the disease
Inadequate treatment can lead to complications. Large cysts cause tissue compression, which impairs nutrition of the lower limbs. This increases the risk of varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
A complication of a tendon cyst on the Achilles tendon can be associated with its rupture. Although synovial fluid does not cause bacterial infection, its leakage into the ankle area leads to acute inflammation. This causes the following symptoms:
The effects of the rupture can last for several weeks. During this time, the uncomfortable symptoms prevent the child from leading a full life.
diagnostic measures.
It usually doesn't take long to diagnose a Baker's cyst. It is diagnosed as follows:
- The doctor listens carefully to the little patient's complaints;
- He asks the parents how long the symptoms have existed and how fast the mass is growing;
- Observes and examines the child's knee joint;
- order an X-ray examination;
- He does a fluoroscopy to distinguish between a cyst and a tumor.
Interesting fact!!!
It is not possible to detect a cyst with an X-ray. Such an examination is necessary to exclude other joint pathologies, including arthritis.
However, if the doctor is in doubt, he or she may recommend additional diagnostics. Sometimes an MRI or ultrasound scan is done.
Causes of synovitis
The main trigger for this disease is traumatic damage to the joint as a result of falls, severe bruises, collisions and other situations in which one or more parts of the joint are damaged. For example, knee bursitis in a child can develop as a result of injury to the soft tissues, muscles and ligaments of the knee, including when blood enters the periarticular capsule (cuts, abrasions, subcutaneous effusions).
Other possible causes of synovitis of the hip, elbow, and other joints in children may include:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the tissues surrounding the joint (phlegmon, carbuncles, boils);
- osteomyelitis;
- Chronic diseases of an infectious nature, including various urogenital diseases, angina and bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Excessive physical activity, especially of a monotonous nature;
- Injuries from sports, dance or other physical activity;
- obesity, which increases the load on the joints;
- chronic autoimmune and endocrine diseases associated with metabolic and micronutrient disorders;
- acute poisoning (poisoning by toxic substances, heavy metal salts, strong drugs)
- postural defects;
- Frequent hypothermia and overheating.
Children with allergic diseases, children with severe bacterial infections at a young age, children with frequent acute respiratory infections are at risk. Students engaged in extreme sports, cycling, martial arts and dance are at increased risk of rebellion if they do not follow safe procedures.
classification
Bursitis can be acute, subacute, chronic, or recurrent. Depending on the cause, a distinction is made between primary bursitis, which results from direct infection of the bursa or trauma to the joint capsule, and secondary bursitis, which is caused by chronic diseases or predisposing factors.
Depending on the type of effusion (synovial fluid), a distinction is made between haemorrhagic, purulent and serous forms. Localization can also play a role, e.g. B. Bursitis of the back of the knee, hip or shoulder, etc.
Other effects of bursitis?
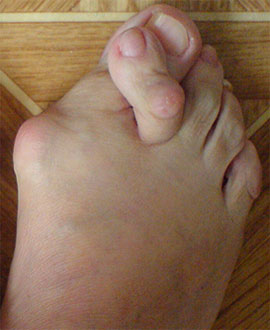
The imbalance between tendons and muscles resulting from the prolapse of the arch of the foot leads to outward deviation of the first toe (hallux valgus), 2-4 toe deformity (hammer toe, claw toe, hammer toe), varus deviation of the fifth toe (Taylor deformity).
| Valgus deformity of toe I, hammer toe deformity of toe II | Valgus deformity of toe I, hammer toe deformity of toes II-IV |
|---|---|
 | 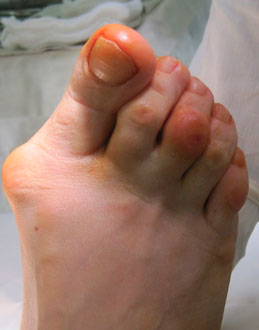 |
Changes in the shape of the arches of the feet, their insufficiency lead to increased pressure on the ligaments and tendons, as well as on certain joints. As a result, degenerative changes - osteoarthritis - develop in these joints.
Due to the flattening of the transverse arch, the heads of metatarsal bones 2-4 fold down. The constant pressure of the heads of the metatarsal bones on the soft tissues causes thickening of the skin under the heads, corns and pain around the heads - metatarsalgia.
Morton's neuroma can result from pressure from the heads of the metatarsal bones on the toe nerve.
| X-ray and appearance of the foot with arthrosis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint | The face of the sole of the foot |
|---|---|
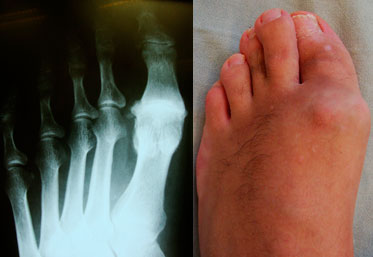 | 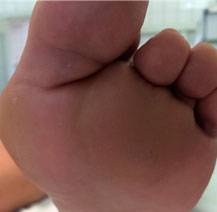 |
What to do if a bump appears on the foot?
A 'bump' can be a symptom of other illnesses, so it's important to first check what is causing it.
As well as the 'bump' there can be other serious changes to the foot that are not apparent at first glance but tend to develop.
The best course of action is the timely visit to an orthopedist.
Accurate diagnosis and qualified treatment can help you get rid of the problem continuous.
video overview
symptoms
The main symptom of any disease is pain. They vary depending on which area of the foot is affected. Bunion is characterized by inflammation of the heel in the sole area. The back of the heel hurts when the Achilles tendon is inflamed. The discomfort worsens with every movement of the foot, preventing patients from walking normally or performing normal activities of daily living. Swelling and redness of the tissues in the affected area are also characteristic symptoms of the disease. A slight swelling is felt on palpation. In some cases, the disease can be accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
causes
Not only athletes, but also normal people can suffer from bunions. Medicine knows the main causes for the development of bunions. The first of these is infectious in nature. For example, after bruises, abrasions and cuts, this disease can occur. Pathogens can easily enter an open wound. In some cases, infection occurs via the lymph following a boil or rust infection. Other causes of the development of the disease:
Mechanical factors also influence the development of the disease, leading to home or hospital treatment. The pathology arises, for example, from wearing uncomfortable shoes. Women who often wear tight shoes with high, unstable heels are particularly susceptible to mechanical synovitis. Synovitis is caused by holding the foot in an unnatural position for an extended period of time.
How the disease is diagnosed
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you should provide the specialist with the following information
- Describe in detail the symptoms your child is complaining of;
- Provide the specialist with information about the patient's physical activity
- Describe any injuries your child suffered
- family history (whether other family members have chronic joint problems, which may be hereditary);
- Describe if the patient is taking any dietary supplements, medications, etc.
The actual diagnosis is made through a physical examination of the pain site by a specialist. The doctor will be able to determine if there is a lump under the knee at the front and if there is any swelling. In addition, the osteopath will correctly assess the range of motion of the knee and hip. In some cases, the patient is referred for an X-ray of the lower limbs. This procedure helps determine how the tendon attaches to the tibia and kneecap.
Primary Treatment Methods
There is usually no specific treatment for Osgood-Schlatter disease: the syndrome resolves spontaneously. Once the bones have finished growing, the pain in the joint is no longer bothersome.
Your doctor can only prescribe treatment for Schlatter's disease if there are clear symptoms. This includes taking certain medications (painkillers), but also physiotherapy and physical therapy. Physiotherapy will help reduce swelling and stop the inflammatory process.
The therapeutic exercises are aimed at gently stretching the tendons and quadriceps. Such exercises can help with pain in the front leg below the knee. In addition, individually prescribed physiotherapy aims to stabilize the knee joint.
Parents and young athletes should prepare for a temporary (until the bone growth phase is complete) lifestyle change:
- Some activities need to be limited because it is important to take the strain off the joint during the active symptomatic phase. Jumping, running or certain sports must be avoided at a certain stage.
- Cold compresses should be applied regularly to relieve pain.
- If it is not possible to abstain from sports, knee pads, elastic bandages and sometimes tape should be used.
- If possible, physical activity should be replaced with something less traumatic. Swimming, cycling, etc. should be considered during this time.
Note that thickening of the leg below the knee may persist even after the disease has ended. Such a lump in no way affects the functioning of the knee joint and does not cause pain. However, there is a risk of the kneecap deforming or moving up. Sometimes this syndrome is complicated by the development of arthrosis.
Read more:- Child has a bump on his foot.
- Shoes for valgus of the child's foot.
- Medial head of the calf muscle.
- The lateral side is.
- Medial and lateral side.
- side of the foot.
- extension and flexion of the foot.
- A child begins to have clubfoot between the ages of 1 and 5.
