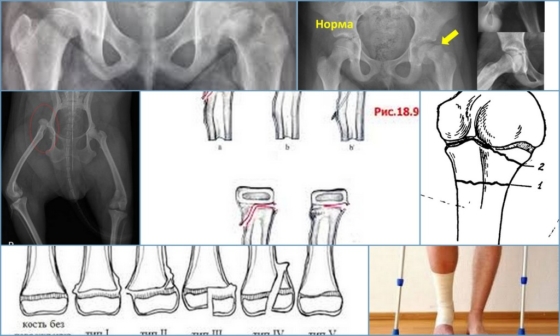
Fractures of the carpal bones are rarely diagnosed; most commonly, the metacarpal breaks in two. The fracture is often accompanied by a dislocation. False joints and cysts often form in the bone at the fracture site. The duration of immobilization is 1-6 months.
- construction of the hand
- Anatomy of the hand skeleton:
- The effects of the treatment are:
- Causes of hand fractures
- Symptoms of a hand fracture
- Fractures of the carpal bones
- Fractures of the navicular bones
- Metacarpal fractures
- Fracture of the first metacarpal
- Removal of spokes and wire after Weber patella osteosynthesis
- Plate removal after surgery
- Hand Fracture Symptoms (Symptoms)
- causes of injury
- Which Doctor Treats Stress Fractures?
- Metacarpal fractures
- Conservative treatment of metacarpal fractures
- treatment methods
- When is surgery necessary for a hand fracture?
- rehabilitation period
- Osteosynthesis at the Miracle Doctor Clinic
- complications
- Treatment
construction of the hand
The bones of the wrist, metacarpals, and phalanges make up the skeleton of the hand. These bony structures are fused together by various types of joints. The long and short (intrinsic) muscles of the hand are connected by tendons to the bony structures of the hand and enable the unique movements of the fingers and hand as a whole. In addition to these three main bone groups, the hand skeleton contains sesamoid bones.
The hand mediates human interactions with the outside world. She can signal the presence of common illnesses and bad habits in a person. Examination of the hand not only provides information about local changes, but also about the condition of the entire body.
Anatomy of the hand skeleton:
- wrist
- scaphoid
- triquetrum
- sicklebone
- pea leg
- Big polygon leg (trapezium leg)
- Small polygonal leg (trapezoidal leg)
- skull bones
- hook bone
- metacarpals
- finger bones
The skin of the hands is often considered an indicator of age. Studies show that a person's age can be determined by the appearance of their hands with an accuracy of up to five years.
Fullness on the hands leads to an accelerated development of deep wrinkles. Due to external factors such as (UV radiation, chemical influences on the skin, temperature fluctuations, etc.), the first age-related changes in the skin on the hands appear long before the 'crow's feet' and nasolabial folds that many people fear.
This process can be slowed down with timely cosmetic treatments.
biorevitalization – An injection treatment in which hyaluronic acid is injected into the middle layer of skin, which forms the nutrient framework for the top layer of skin.
The effects of the treatment are:
- The skin is visibly smoother and firmer;
- The visibility of veins is reduced;
- pigmentation is smoothed;
- The skin turgor is improved (lifting effect),
- the feeling of dryness disappears.
Sources: https://totispharma.com/, https://virtusclinic.ru/, https://leyla-roz.ru/, https://skin.ru/, https://virtusclinic.ru/, https:/ /meduniver.com/, https://www.elib.vsmu.by/
Causes of hand fractures
- Fall onto an outstretched upper limb
- heavy push
- car accident
- Sports or work-related injuries
The broken hand bones may or may not be displaced. An open injury is characterized by a wound surface with protruding bone fragments. More common closed injuries are characterized by the absence of a superficial wound. The integrity of the joints can be compromised by the fracture.
Symptoms of a hand fracture
Depending on the area of damage, this disease has a different appearance and is accompanied by specific symptoms. For example, if the scaphoid, triquetrum, and crescent bone are damaged, mobility of the upper limbs in the wrist is reduced because these anatomical structures are part of the wrist. The main symptom is a pain syndrome. The pain can occur at rest and increases with movement.
- acute pain when touching the hand or wrist
- Deformation of the fingers with limited motor skills
- Sensation of a bone fragment in the area of the anatomical snuff box at the base of the thumb
- swelling, bruising
It is difficult to identify the affected area and differentiate between a fracture and an anatomical disorder based on symptoms alone. The doctor uses this information to make an initial diagnosis. Objective investigations are required to identify the affected anatomical structures.
Fractures of the carpal bones
Because of their shape, structure, and location, the carpal bones rarely break. The scaphoid — the large bone at the base of the thumb — is most commonly affected by fractures. Fractures of the crescent and pea bone of the wrist are also common. The triangular bone and the bones of the distal row - the polygonal, trapezoidal, parietal and hamstring bones - are extremely rare and are usually associated with dislocations of the corresponding joints.
Fractures of the navicular bones
Caused by a flexed-hand fall, a punch, or direct trauma to the wrist. Possible variants are:
- Intra-articular fracture of the scaphoid – the fracture line is within the joint cavity of the wrist;
- Extra-articular fracture – a tear in the navicular bone;
- De Kerwen fracture – simultaneous fracture of the navicular bone and displacement of its proximal fragment and carpal bone from the carpal joint.
Symptoms include pain and swelling at the base of the thumb, an inability to move the hand in the wrist, and an inability to make a fist. The diagnosis is made based on the patient's symptoms, the nature of the injury, examination, and X-rays of the carpal bones. If there is no displacement of the fragments, sometimes the line of fracture cannot be determined with all the signs. In this case, immobilization is maintained, and X-rays are repeated after 7-10 days, when the fracture line becomes clearly visible due to the activation of the regenerative processes.
Treatment consists of immobilization with a cast for 4 weeks, followed by monitoring and prolongation of immobilization if fracture consolidation is insufficient. In the case of displaced fractures and fracture detachment, closed reduction is ineffective and immobilization of scaphoid fractures with a spoke is indicated. Fractures of the heel bone are often complicated by the formation of a false joint or lysis of the bone fragments due to damage to the blood vessels that supply them during the injury. That is why it is so important to follow all the doctor's instructions and take x-rays in a timely manner in order to avoid complications and deterioration in the functioning of the wrist. After metacarpal repair, physiotherapy and physical therapy are indicated to restore wrist function.
Metacarpal fractures
The long and slender metacarpal bones are commonly fractured from a punch or as a result of direct trauma. Muscle tension and hand movements prior to fracture immobilization often result in displacement of the bone fragments. A distinction is made between epiphyseal fractures, where the fracture line is in the area of the bone heads, and diaphyseal fractures, where the bone shaft is broken.
Fracture of the first metacarpal
Caused by a bent first finger, more rarely by a direct blow to the first metacarpal.
Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal. A typical injury in boxers and MMA fighters. A distinction is made between a Bennett fracture, in which the base of the first metacarpal, which is held by ligaments, is torn, and a simultaneous dislocation of the large metacarpal in the carpal joint. The Roland fracture is a multiple fracture of the first metacarpal. Both injuries present with pain, deformity and swelling in the 'anatomical snuffbox' - the area under the base of the first finger - with increasing pain with movement and attempting to clench a fist. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, history of injury, examination of the area of injury, and X-rays of the hand. Bennett and Roland fractures are treated surgically with osteosynthesis, that is, the integrity of the bone is restored by fixing the fragments with metal pins, pins or plates.
Fracture of the middle part of the first metacarpal. Most often it is caused by a direct blow to the bone. It manifests itself as pain, swelling and deformation in the area of the first metacarpal. The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints, information about the mechanism of injury, examination of the first metacarpal, and x-ray of the hand bone. Treatment consists of cast immobilization for 4-5 weeks; if the fragment is displaced, a closed reduction is performed first. If conservative repositioning is ineffective, an operation is performed to reunite the fragments – spiral osteosynthesis.
Example of one by Dr. Valeev performed surgery to heal a fracture of the first metacarpal:
Removal of spokes and wire after Weber patella osteosynthesis
In the case of kneecap fractures with dislocation, osteosynthesis, i.e. the fixation of bone fragments, is carried out in order to restore the integrity of the bone and thus the function of the knee joint. If the operation is refused, there is a risk that the patient will remain disabled.
In most cases, the Weber technique is used for patellar osteosynthesis. Two titanium Kirschner pins are attached to the bone fragments and clamped together with a titanium wire 8 . In this way, the damaged bone can be restored quickly and very effectively, and - just as important - the metal construction is very inexpensive. However, it has one major disadvantage. Very often patients experience discomfort and pain in the bone and wire area because the wire is just under the skin. For this reason, the metal structure is often removed from the kneecap.
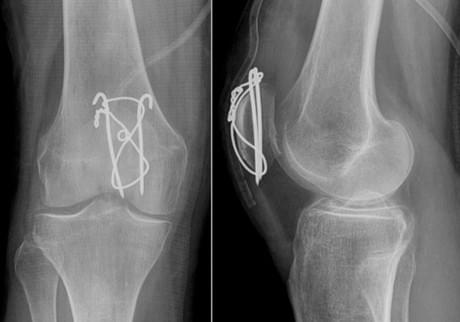
Once the bone has healed and the steel structure has served its purpose, it can be removed. Complete healing of the bone occurs within 6-8 months, in some cases up to a year. The metal can only be removed after this time.
The usual blood tests must be carried out before the operation; a list of these examinations can be found here.
The operation is often performed in a day center, so the patient can go home just a few hours after the operation. Anesthesia is local, either through a wire or through anaesthesia. The operation itself takes about 30 minutes. Locating the wire and spokes is usually not difficult for the surgeon. Once the metal structure is removed, the wound is stitched and an aseptic bandage applied. The patient is bandaged for the first 24 hours, after which he can look after himself or be treated at a hospital near where he lives. The sutures should be removed 14 days after the operation. Painkillers and antimicrobial drugs are administered in the early postoperative period.
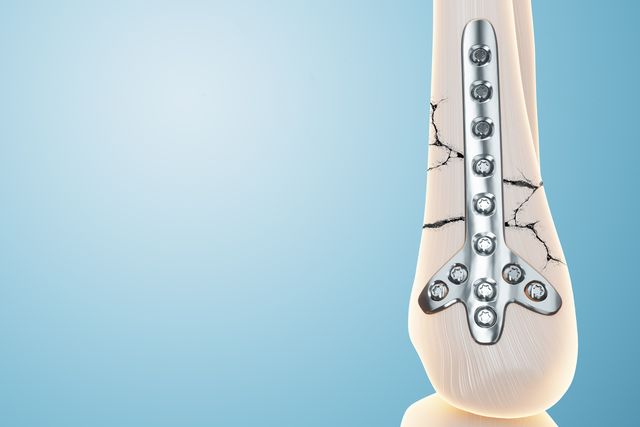
Plate removal after surgery
Plates and screws fix almost all bones in the human body. It is a very safe and convenient method of osteosynthesis. There are now a large number of plates of different shapes, sizes and modifications for each type of fracture. The most common examples of plate osteosynthesis are:
- osteosynthesis of the clavicle;
- Osteosynthesis of the humerus
- osteosynthesis of the lateral malleolus;
- Internal fixation of lower leg fractures;
- Osteosynthesis of the metacarpal and metatarsal bones;
- Osteosynthesis of the radius and elbow bones.
The plates are usually removed 8-12 months after surgery.

Hand Fracture Symptoms (Symptoms)
Fractures of the hand bones can manifest themselves in different ways. For example, when the scaphoid is damaged, the thumb joint becomes swollen and painful, or the metacarpals and phalanges become blue and swollen. With a deformity of the sickle bone, the swelling is insignificant, but moving the fingers is painful. Despite these differences, however, common symptoms of a broken hand can be distinguished:
- pain and swelling;
- inability to move fingers freely;
- difficulty clenching your fingers into a fist;
- blue discoloration of the skin at the site of injury;
- Obvious deformation of the affected area;
- Abnormal bone mobility.
In many cases, the swelling is not only visible at the site of the injury, but also far beyond in the direction of the elbow. An open fracture is a wound in the skin. Bone splinters may protrude from this wound. Do not attempt to repair the fracture yourself as the wound can easily become infected. A simple treatment to stop the bleeding is to apply a bandage or bleeding gauze.
causes of injury
The most common cause of hand fractures is a fall or severe blow to the hand. Because the 27 bones that make up the hand are thin and unstable, with little soft tissue around them, they can take the brunt of the impact when force is applied. As a result, they break and break. Each damage to a bone has its own peculiarity. An example is the fracture of the heel bone:
Toe bone fractures occur when the toes are pressed against a tool or door, or when a heavy object falls on them. A fracture of the toe bones can cause pain:
When the base of the metacarpal is broken, there is severe pain in the hand due to the complexity of the injury. This bone can:
Damage to the remaining metacarpal bones results in hand deformity. However, the pain in this case is milder than with injuries to the first metacarpal. These fractures result from a strong direct punch or a fall on the hand. Other parts of the hand are less likely to break because they form an arch and are reinforced by tight ligaments.
Which Doctor Treats Stress Fractures?
If your hand is swollen and deformed after a fall on ice, pavement, or a blow, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. It is very likely that there is a fracture of the hand. Only a specialist doctor, based on his examination, can confirm or refute this diagnosis. Patients with these symptoms are admitted to the hospital:
Metacarpal fractures
- MENU OF DEPARTMENTS
- Allergology-Immunology
- Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (conjunctivitis)
- Allergy to grass pollen
- Allergic dermatitis
- Allergy to pets
- Allergy to house dust and its components
- Allergy to insects
- Allergy to pollen
- Allergy to tree pollen
- Allergy to grass pollen
- Eczema and other immune-mediated dermatoses
- Allergy to insect bites
- angioedema and Quincke's edema
- Atopic dermatitis
- immune disorders
- Allergy to drugs
- Acute and chronic urticaria
- Early signs of allergy
- Allergic alveolitis
- Why do my ovaries hurt and what can I do about it?
- Dysplasia of the cervix
- How to prepare for a visit to the gynecologist?
- Causes of abdominal pain
- ovarian apoplexy
- Bartholin's inflammation, cyst or abscess
- ectopic pregnancy
- hematoma
- hydrosalpinx
- Hyperplastic endometrial processes (hyperplasia, polyps)
- Leukoplakia of the cervix
- endometritis of the uterus
- Uterine fibroids
- menstrual disorders
- Ovarian tumors (cysts and cysts)
- Prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina
- Polycystic ovaries
- cervical polyps
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy
- endometriosis
- Cervical erosion and ectropion
- Current approaches to the diagnosis of cervical abnormalities
- sinus infection
- Chronic rhinitis
- Nasal furunculosis
- pharyngitis
- inflammation of the tonsils
- Polypoid stomatitis
- otitis media
- acute rhinitis
- nosebleeds
- laryngitis
- Distorted nasal septum
- ENT diagnosis
- Opening of a parotid abscess
Conservative treatment of metacarpal fractures
Fractures without displacement are treated in plaster for 4-6 weeks. At the end of this period, follow-up imaging studies are performed to assess treatment outcomes and rule out secondary fracture displacement. After the plaster cast is removed, there may be a certain restriction of movement in the metatarsophalangeal joints, which requires movement development with special exercises and physiotherapy. Conservative treatment is also possible with appropriate repositioning (juxtaposition) of the displaced fractures.
If the broken bone is deformed in length, width, or angle, osteosynthesis with a plate, screws, or spikes is indicated, and if there is a diaphyseal fracture, fixation with a plate and/or screws, where a pin can be inserted into the bone. If the plate causes discomfort to the patient, it can be removed, but not before the end of a year. In most cases, however, the metal brackets cannot be removed. The insert is placed intraperiosteally (inside the core canal) for approximately 4-6 weeks. This immobilization will be removed after the x-rays have been taken and the bone has healed.
It is possible to fix the fragments with pins through small punctures in the skin if adequate closed reduction (juxtaposition) of the fracture is possible. The ends of the pins usually protrude above the skin, but can also be dipped under the skin. These metal fixators are removed after the fracture has healed, approximately six weeks after placement. The main advantage of this method is that no skin incisions are made during the operation. Regardless of the fixation method chosen, the patient can usually only start activities in the finger joint a few days after the operation.
The final choice of the osteosynthesis method is left to the treating physician and depends on the medical indication, the type of fragment displacement and the functional requirements of the hand.
treatment methods

With a fracture of the hand bone, it is necessary to fully restore the function of the injured limb. For this purpose, the bone fragments are repositioned, a plaster cast is applied and rehabilitation is initiated. Bone repositioning is performed under local anesthesia, more rarely under general anesthesia.
A cast is applied from the head of the metacarpal bone to the upper third of the forearm. The thumb is fixed on the cast. After two to three weeks, the patient is examined with a second x-ray.
If a cast is not put on properly, it can have long-term consequences. If the bandage is too tight, it squeezes the tissue and causes compression of the blood vessels. Within a few weeks of immobilization, the articulation disappears due to compromised blood flow and an ischemic contracture develops.
If the cast or splint is too loose, the patient will move the wrist involuntarily. This leads to displacement, insufficient bone fusion, and disruption of the anatomy of the hand.
A complication of an open fracture of the hand can be osteitis. The disease develops when bacteria penetrate the bone tissue from the outside and a cavity with pus forms. Symptoms include severe, persistent pain, high body temperature, and signs of severe intoxication. Bone density decreases, often resulting in a second fracture at the site of the first.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain, and if these do not help, glucocorticosteroids are used. To accelerate the regeneration of bone tissue, chondroprotective agents and calcium supplements should be taken.
When is surgery necessary for a hand fracture?
If complications are detected, surgical intervention is required. There are several types of intervention:
- osteosynthesis. During the surgery, the edges of the broken bone are held together with staples or metal pins. A plaster cast is then applied for immobilization.
- bone graft. Whole bone tissue from the patient or a donor or an artificial implant is placed in the damaged area. This accelerates the regeneration process of the damaged bone.
- arthrodesis. This operation is performed in case of multiple fragment fractures of the hand. The bones are held in place by artificial immobilization and the joint is not displaced.
- Endoprosthetics – damaged bone structures are replaced with artificial implants.
The doctor selects the surgical procedure for each patient individually. The age and general condition of the patient, the type of injury and any contraindications are taken into account.
rehabilitation period
The doctor creates an individual rehabilitation program for each patient. Rehabilitation is most effective if it starts on the 2nd or 3rd day after osteosynthesis surgery. It is extremely important that the doctor's instructions are followed exactly!
Recovery time depends on a number of factors:
- the complexity and location of the fracture;
- the surgical technique and execution used
- Age and general condition of the patient and concomitant diseases;
- how quickly the healing process progresses.
The rehabilitation period can be divided into several phases:
- postoperative period. Lasts 2 to 5 days and includes full recovery of the patient. During this period, swelling, fever, malaise, hematoma, weakness and pain may appear. Usually, such conditions are treated as normal after surgery and no further intervention is required. On the third day, you should start moving the operated limb. First, all manipulations are performed under the supervision of the doctor, then the patient begins to independently bend and straighten the arm or leg, as well as rotate it. Gradually, the load increases.
- At the start. Lasts 2-3 weeks after surgery. The patient remains in the hospital during this time. The doctor monitors the patient's condition in order to detect and prevent possible complications as early as possible. If healing progresses well, the sutures are removed and the patient is discharged.
- Mobilization. Lasts 2-5 months after osteosynthesis. The patient is treated on an outpatient basis and undergoes various complex rehabilitation measures.
- period of functional recovery. This usually occurs after six months. By this time, the function of the limb is fully restored, so rehabilitation measures are aimed at strengthening muscles, restoring proper coordination of movements, restoring and improving skills for daily life and work.
Osteosynthesis at the Miracle Doctor Clinic
If this treatment is indicated for you, we recommend surgery at the Miracle Doctor Clinic. We guarantee individual treatment that takes into account the fracture, the condition of the bone and the general condition of the body.
- Thanks to the minimally invasive techniques we use, we can perform stable and functional osteosynthesis at an early stage after the injury.
- Thanks to the stability of osteosynthesis, patients can be activated in the first hours after surgical intervention, which facilitates care, improves the course of traumatic disease and reduces the risk of developing severe hypostatic complications.
- The use of minimally invasive biological osteosynthesis can significantly shorten the length of stay in hospital and significantly improve the quality of life of patients in the early postoperative phase.
Affordable internal fixation, a personalized approach, highly skilled trauma surgeons, and attentive and caring staff help minimize the consequences of the injury and restore confidence in recovery.
complications
If not treated early, epiphysiolysis can lead to serious health problems and disabilities. The affected bone stops growing in length and deforms the affected leg. A second serious complication is the death of the affected tissue and the development of gangrene.
Important!!!
If osteoepiphysiolysis is diagnosed and treated at an early stage, the prognosis is good.
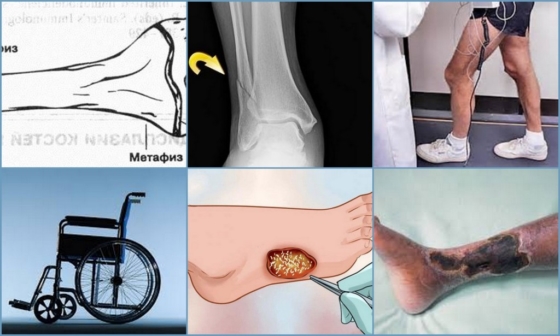
Treatment
If an epiphyseal fracture develops, the patient needs urgent medical attention. Treatment depends on the stage of the disease. The first five types of epiphysiopathy are the most common and are treated accordingly:
- Type I - in a transverse fracture, a spoke is inserted to immobilize the epiphysis;
- Type II - in this form, a plaster cast is sufficient;
- Type III - a severe lesion requiring immobilisation of the partially fractured condyle with a screw;
- Type IV - the fully fractured epicondyle is fixed by skeletal traction followed by internal fixation of the head with a pin and graft;
- Type V - a compression fracture without displacement is immobilized with a cast.
All of these surgeries are performed with minimal tissue excision. Open surgery is not recommended because of the high risk of infection and necrosis of the bone head and loss of joint function.
A timely visit to the doctor in case of epiphysiolysis is a guarantee of a speedy and full recovery. Self-treatment can worsen the patient's condition and lead to disability.
- metatarsal and metacarpal bones.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- Fracture of the calcaneus of the foot.
- Bone structure of the navicular foot.
- tibia and fibula.
- Inflammation of the tibial cortex.
- Shoe prophylaxis - what is it?.
- The bones of the human heel.
