In complicated situations (open injury with dislocation), surgery is indicated.
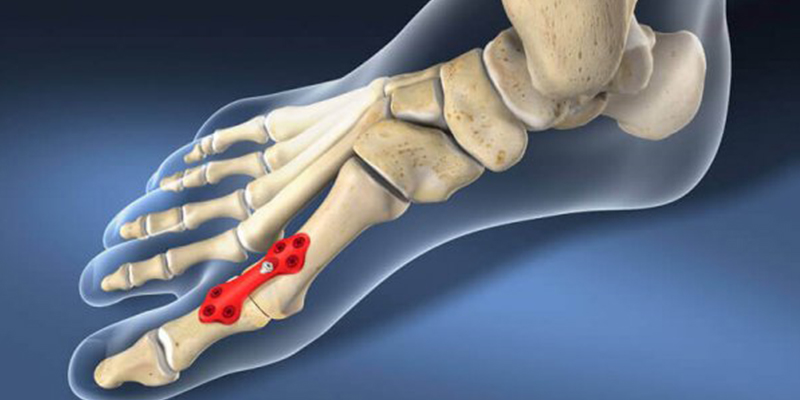
- Treatment of foot pathologies
- Valgus deformity of the first toe or valgus'.
- Why do feet hurt?
- Hallux valgus (Hallux valgus)
- diagnosis
- First aid for trauma
- Treatment
- surgery
- Plaster cast .
- Foot orthosis for metatarsal fractures
- Anatomy of the Human Foot – Information:
- Which doctors can you go to to have the bones of the foot examined?
- Human Toe Bone Anatomy Information:
- Which doctors should you go to to have your finger bones checked?
- Fractures of the forefoot bones
- Fractures of the metatarsal bones (metatarsal fractures)
- treatment methods
- recovery period
- External foot pain
- Causes of pain in the foot on the outer lateral side
- diagnosis
Treatment of foot pathologies
First, let's discuss some diseases caused by different types of forefoot deformities and their treatment.
Let’s go over some of the most common forefoot problems.
1. the hallux valgus or hallux valgus (or valgus' as it is often called by patients)
2. hammer toe and forefoot pain or metatarsalgia, which are often directly related to hallux valgus.
3. Hallux Rigidus, a localized degenerative disease of the big toe. Deformity, stiffness and chronic pain at the base of the first toe.
4. the heel spur or plantar fasciitis.
In most cases, we prefer conservative treatment methods, and only when results are not achieved, surgical techniques are considered.
Valgus deformity of the first toe or valgus'.
Many people are familiar with this condition. The 'ankle', as patients call it, is a syndrome of deformities and biomechanical problems in the forefoot, often caused by wearing uncomfortable shoes:

We should not forget about genetic predisposition, that is, if your mother or grandmother had similar problems, there is a high probability that this pathology will also occur in you.

Why does the deviation of the first toe continue to progress?
Normally, the first toe takes on much of the load when walking. It's like pushing off from a surface and leaning on your first toe. The force caused by the contraction of the lower leg muscles is transmitted to the toenail phalanx of the first toe via the flexor tendon.
BUT!!! With a significant deformation (see figure), the flexor tendon of the first toe becomes like the tendon of a bow, that is, the tension increases the curvature of the bow.
With each step, the deformation of the first toe increases, resulting in an ever-increasing deformation and outward deviation.

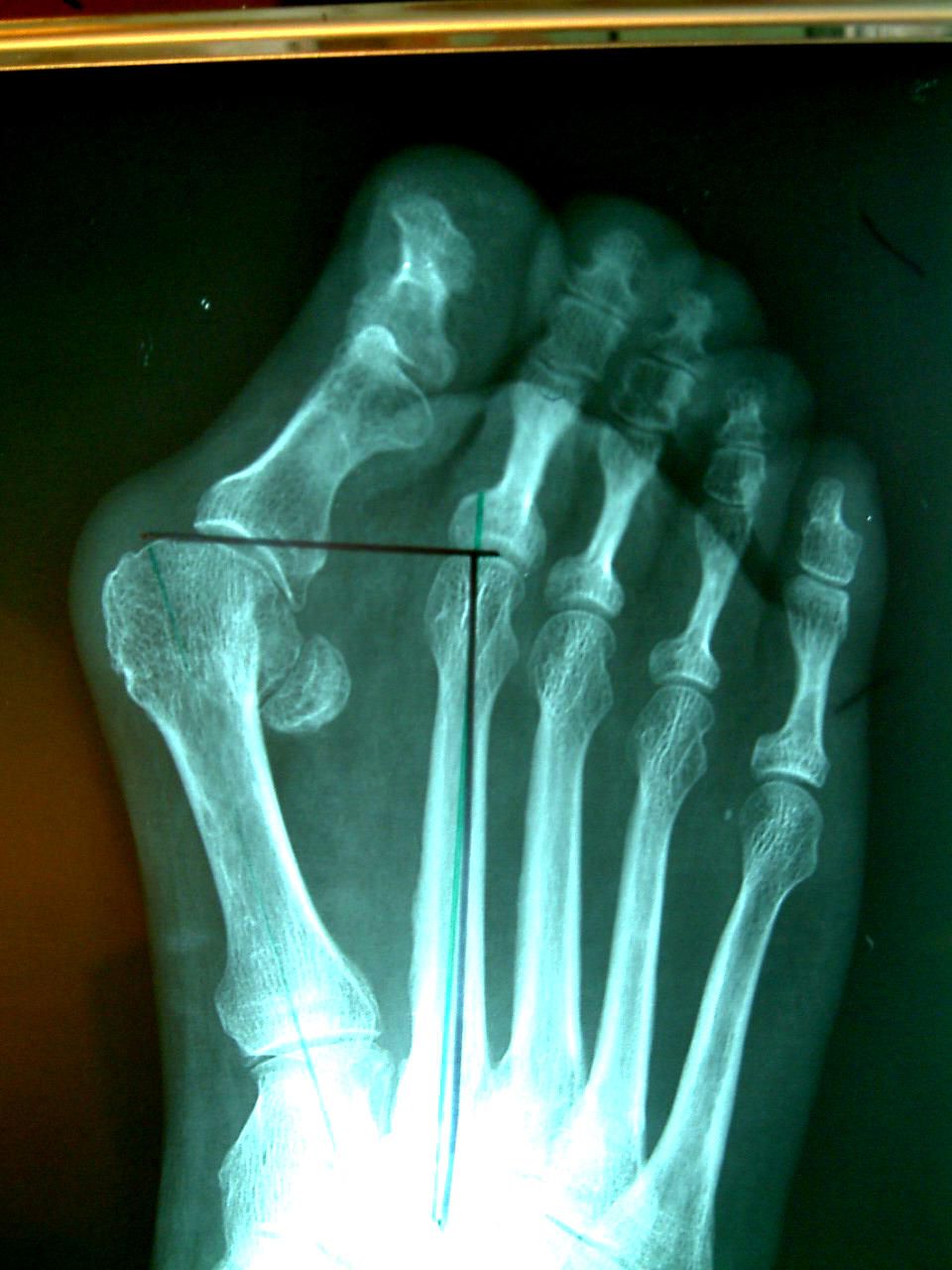
The drawing and x-ray show a small round sesamoid bone between the metatarsals. This lies in the thickness of the flexor tendon of the first toe and is normally located under the head of the first metatarsal, but the progressive deviation of the first toe causes this tendon to shift and its tension during walking increases the deviation of the toe.
Why do feet hurt?
The causes of foot pain are varied, but three groups of factors can be distinguished:
- Hereditary predisposition is a common factor in the development of foot deformities at any age.
- External factors – these include lifestyle, physical activity, type of footwear most commonly used and the effects of trauma.
- Triggering factors – these include general diseases such as rheumatism, diabetes and neuromuscular disorders (including stroke).
In most cases, it is the combination of these factors that causes the foot to 'wear out' faster than the rest of the body, resulting in bony deformities of the foot, pain and inflammatory changes in the joint capsule (bursitis).
Our clinic specializes in modern, minimally invasive surgery for various bone deformities of the foot. We have extensive experience in both conservative and surgical treatment of foot diseases and therefore believe it is necessary to share all information so that patients can make the right decision in a timely manner.
You can schedule an appointment with an orthopedic trauma surgeon by calling 8(495)414-20-64or make an appointment by filling out the online form.
Hallux valgus (Hallux valgus)
One of the most common foot abnormalities is an outward deviation of the big toe. (hallux valgus). Often this deformity is of cosmetic importance and is not associated with pain.
However, the constant traumatization of the joint capsule at the base of the first toe leads to irritation and inflammation, which causes pain, even very severe pain, against the background of rich innervation, that is, hallux valgus is most often accompanied by bursitis (inflammation of the periarticular capsule; the term 'bunions' - 'tumour, painful capsule' - is also used).
The causes of hallux valgus include a congenital predisposition and the wearing of shoes per se, especially uncomfortable and traumatic shoes. The ratio of 1:10 to 1:15 between men and women can also be explained by women wearing high-heeled and narrow shoes.
In the pathogenesis of hallux valgus, there is an outward deviation of the big toe from the first metatarsal, an inward and often upward displacement of the first metatarsal in relation to the second metatarsal, and the formation of growths on the inner and posterior side of the head of the first metatarsal bone.
In addition to the factors mentioned above for the development of hallux valgus (hereditary predisposition, external factors, general diseases), flat feet, arched feet and a short Achilles tendon also play a role. All of these factors can lead not only to an outward displacement of the big toe and an inward displacement of the first metatarsal, but also to an upward displacement of the first metatarsal. This causes the big toe to lose its normal 50 percent load on the foot, resulting in weight being redistributed to structures that are not designed for it. This increases pain and inflammation, closing the pathological circle (inflammation produces pain and vice versa).
diagnosis
The choice of examinations determines the correct treatment of the patient and the avoidance of complications. Depending on the clinical picture, the patient may undergo the following examinations
X-ray examination – The basic examination carried out for foot injuries. The information contained therein is often insufficient. An early stress fracture may not be visible on conventional radiographs, or there may be a small periosteal reaction that is easily missed. The examination shows a fracture of the metatarsal bone, but is not suitable for diagnosing injuries to the soft tissues and ligaments.
A computer tomography provides more information about the pathology. The indications include the suspicion of a stress fracture with unclear X-ray findings. CT scan shows burst injuries, splinter injuries, and any bone pathology.
MRI – is the most informative method for examining complex foot injuries with soft tissue involvement and ligament tears/strains. MRI shows bone marrow swelling earlier than CT. MRI is the best method for visualizing stress fractures of the foot and is suitable for differentiating synovitis from degenerative changes. The combination of MRI and CT is optimal for obtaining a complete picture of the components of the foot - tarsal bones, metatarsals, phalanges, hard structures and soft tissues.
The ultrasound examination is used in trauma care because it is easily accessible and easy to use, but it is not suitable as a sole diagnostic tool.
First aid for trauma
If a limb is injured in the foot area, a doctor should be called immediately. Before the doctor arrives, first aid should be given to the injured person. To do this, you should do the following when providing first aid:
- Immobilize the injured leg as much as possible.
- Apply cold to the injured area. Ice should be applied for no more than 20-30 minutes, the interval between compresses should be one and a half hours. Otherwise, frostbite and necrosis may occur.
- Apply a bandage. Do not wrap the elastic bandage too tightly so as not to constrict the blood vessels.
- Raise the limb above the body and immobilize it: this will help reduce swelling and numb the pain.
If possible, take the patient to the local emergency room without waiting.
Treatment
Treatment for a fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone depends on the type and severity of the injury. If there are no sprains, splinters, or open wounds, the injury will heal quickly. Acute pain is treated with painkillers in the form of tablets, ointments and gels for external use. Physical stress on the injured leg should be limited until the bone heals. The limb is immobilized with a plaster cast and the patient can move around with crutches. After another X-ray examination and confirmation that the bone has healed, the patient can put weight on the injured leg again. Special orthoses are recommended to relieve pressure.
Also read: What to do if a child twists an ankle and limps?
Surgery is indicated for fractures with displacement or skin damage.
surgery
This is carried out when the bone pieces are displaced from each other by more than half their width. During the operation, they are assembled in the correct position, secured with special connectors and then the spokes are inserted. After the manipulation, the surgical incision is sutured (no plaster is used). The patient is able to walk independently for a month.
Plaster cast .
This is a firm plaster cast that is applied from the ankle to the toes. It serves to immobilize the broken bone, prevents further separation of the fragment and protects the limb from accidental bumps and bruises. A plaster cast is worn continuously for 4-6 weeks.
Foot orthosis for metatarsal fractures
For minor fractures (without displacement and soft tissue destruction), a foot orthosis should be used. It is more aesthetically pleasing, allows the foot to be immobilized and reduces the load on this part of the body. With multiple fractures of the metatarsal bones, the use of such fixation devices is unacceptable.
Anatomy of the Human Foot – Information:
The human foot is the lowest part of the lower limbs. The part of the foot that is in direct contact with the ground is called the foot or sole. The foot is made up of the tarsal, metatarsal and toe bones.



Which doctors can you go to to have the bones of the foot examined?
Are you worried about something? Would you like to learn more about the bones in your feet or do you need an examination? You can make an appointment with your doctor – Clinic Eurolaboratory is always there for you! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary care and diagnose the problem. You can also doctor at home. clinic Eurolaboratory is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic:
The phone number of our clinic in Kiev: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multichannel). The clinic's secretariat will find a suitable day and time for you to see a doctor. Click here for our coordinates and directions. Further information about all of the clinic's services can be found on the clinic's homepage.
If you have been examined before Be sure to bring the results with you to your doctor's office. If you have not yet done any examinations, we will carry out the necessary work in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is important that you take a very close look at your general health. There are many diseases that do not initially manifest themselves in our body, but unfortunately are treated too late. It is enough if you go to the doctor several times a year Go for a medical check-up several times a yearIt's important to get checked up several times a year, not only to prevent a serious illness, but also to maintain a healthy body and mind.
If you want to ask your doctor a question, use the online guide, where you will find answers to your questions and read Self Care Tips. If you are interested in opinions about clinics and doctors, you will find the information you need in the forum. Also register on the medical portal Eurocoolto stay up to date with the latest finger bone news and information, automatically delivered to your inbox.
Human Toe Bone Anatomy Information:
The toe bones, phalanges, phalanges digitorum pedis (eng.. (short tubular individual finger bones), differ from similar bones in the hand in their small size.

The toes of the foot, like those of the hand, consist of three phalanges, with the exception of the first toe, which has only two phalanges. The distal phalanges have a thickening at their end, the distal phalangal tuberosity, which is their main distinguishing feature. The sesamoid bones are located in the metatarsophalangeal joints of the big toes (around the first finger) and in the interphalangeal joint of the first finger.

Deposits. The radiological picture of the age-related changes in the skeleton in the area of the foot and ankle joints corresponds to the successive appearance of ossification points in the calcaneus at 6 months, talus at 7-8 months, cuneiform at 9 months, cuneiforme laterale at 1 year of life, in the distal tibial epiphyses at the age of 2 years (synostosis at the age of 16-19 years), in the distal sagittal epiphyses at the age of 2 years (synostosis at the age of 20-22 years), in the short tubular epiphyses at the age of 2-3 years (synostosis in age 20-25 years), in the medial cuneiforms at the age of 2-4 years, in the cuneiform intermedium at the age of 3-4 years and in the naviculars at the age of 4-5 years.
Some peculiarities of the ossification of the foot skeleton should be noted: The calcaneus has an apophysis, tuber calcanei, which develops from several points of ossification, appears at the age of 7-9 years and fuses with its shaft at the age of 12-15 years; separate bone nuclei are found in the posterior tali process, in the apophysis of the navicularis bone, tuberositas ossis navicularis, in the apophysis of the fifth metatarsal bone, tuberositas ossis metatarsi quinti. During the time that these bone cores exist, they can be mistaken for bone fragments. In this context, the sesamoid bones of the I finger should also be considered, which ossify in girls at the age of 8-12 and in boys at the age of 11-13. Due to the reduction in size, the V-finger often only has two phalanxes - a two-finger phalanx.
Which doctors should you go to to have your finger bones checked?
Is there anything that worries you? Would you like to learn more about the bones in your toes or have an examination done? You can make an appointment with your doctor – Clinic Eurolaboratory is always there for you! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary care and diagnose the problem. You can also doctor at home. clinic Eurolaboratory is open for you 24 hours a day.
How to contact the clinic:
Phone of our clinic in Kiev: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multichannel). The clinic secretary will find a convenient day and time for you to see a doctor. Click here for our coordinates and directions. Further information about all of the clinic's services can be found on the clinic's homepage.
If you have ever had an examination carried out, Be sure to bring the results with you to your doctor's office. If you have not yet done any examinations, we will carry out the necessary work in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is important that you take a very close look at your general health. There are many diseases that do not initially make themselves felt in the body, but unfortunately in the end it is too late to treat them. To do this, it is simply necessary to be examined several times a year Have yourself examined by your doctor several times a yearto not only prevent a terrible disease, but also keep your body and your entire organism healthy.
If you want to consult a doctor, you can find and read answers to your questions on the Internet Self Care Tips. If you are interested in clinic and doctor reviews, you can get information in the forum. You can also go to the medical portal EurocoolSign up to stay up to date with the latest finger bone news and information automatically delivered to your inbox.
Fractures of the forefoot bones
Fractures of the scaphoid, cuboid and sphenoid bones are most often caused by direct trauma - a fall on the foot with a load. Fractures of the navicular bone can also be caused by indirect trauma - with excessive flexion of the foot, the foot is compressed and breaks in the horizontal plane, displacing the bone fragment forward. A sudden contraction of the tibialis posterior muscle results in a rupture of its tuberosity at the tendon insertion site. As a rule, the fractures of these bones do not cause any significant displacement, but they weaken the longitudinal arch of the foot.
symptoms. Examination reveals swelling of the foot and subcutaneous bleeding at the impact site. Local pain on palpation. A subluxated fragment of the meniscus bone may be palpable. The pain increases with movement of the distal part of the foot (when the fifth foot is stationary) or with axial loading of the metatarsal bone. The location of the fracture is clarified radiographically in two or three projections (if the tubercle is detached). Sometimes a fracture of the sesamoid bone in this area of the foot is seen as a tuberosity fracture. Therefore, a comparative radiograph of the other foot should be taken to differentiate the two cases. There are cases when no fracture of the ischium is detected, so it is sometimes necessary to repeat the x-ray in a different projection.
Treatment. If there is no displacement of the bone fragments of the splint, a plaster cast with a well-modeled longitudinal arch of the foot is applied for 3 weeks. This is followed by physiotherapeutic and balneotherapeutic treatment. The duration of the inability to work is 4-5 weeks. Shoes with supinators must be worn for one year.
In case of. Subluxation and dislocation of a fracture of the scaphoid The reduction is carried out under local anesthesia above the carpal bone head. The foot is pulled axially and flexed distally, and with two fingers the protruding fragment is compressed and pushed inward. After repositioning, the foot is brought into the central physiological position. However, since the subluxation has a tendency to recur, it is better to fix the fracture of the carpal head immediately after reduction with two or one K-wire through the skin and apply a plaster cast. The spokes are removed after 3-4 weeks and the plaster cast after 2.5-3 months. The patient then undergoes reconstructive therapy. It is possible to return to work 3-4 months after the injury.
Fractures of the metatarsal bones (metatarsal fractures)
Metatarsal bones most often break when the body is exposed to direct trauma - pressure or impact with a heavy object. Fractures of one or more bones can occur at the same time. Fractures most often occur in the diaphysis and neck of the metatarsal bone, less often in the base and head of the metatarsal bone. Avulsion fractures of the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal are also common. If one or two bones are broken, there is no significant displacement of the fragments because they are supported by the neighboring intact bones. It is very disadvantageous to place fractures at an angle that is open to both the sole and the opposite side, as normal footwear puts pressure on the exposure of the abnormally healed bone and causes pain. This is particularly common with fractures of the metatarsal neck.
symptoms and diagnosis. The diagnosis of a metatarsal fracture is made based on the history and clinical symptoms, which in turn depend on the severity of the injury and the number of bones broken. The foot is swollen with bleeding on the erect surface, and the skin is sometimes damaged. Extension of the foot is impossible due to pain. On palpation there is a sharp local pain that increases with axial pressure on the bone. The type and location of the fracture is clarified using a double projection x-ray.
Treatment. For fractures with little or no displacement of the fracture width, a plaster cast is applied under local anesthesia, which well models both the longitudinal and transverse arch of the foot. A radiological follow-up check is carried out.
After 5-6 weeks, the cast is removed, restorative treatment is recommended, and the foot is supported with supinator shoes. Duration of incapacity for work
2-3 months, depending on the number of fractures.
fractures diaphyseal and metatarsal necks with displaced fractures are repaired under local anesthesia. Traction along the bone axis and lateral correction with the hand is effective in most cases. The 1st and 5th metatarsals must be reduced particularly carefully. Metatarsal bones must be reduced particularly carefully. However, a plaster shoe does not provide a secure hold for the reduced fragments, especially in the case of oblique fractures of the diaphysis and the necks of the metatarsal bones. They are therefore fixed with Kirschner pins (one in each bone), which are inserted from the sole or interdigital side through the skin and head into the diaphyseal bone. A plaster cast is applied and treated as with fractures without displacement.
treatment methods
The choice of treatment methods depends on the type, severity and age of the injury:
- If there is a fracture without dislocation, a plaster cast is applied immediately.
- For a displaced foot fracture, open or closed fracture reduction is performed under local anesthesia. A plaster cast is then applied.
- Skeletal traction. Used in long-term trauma when closed reduction is ineffective.
- Osteosynthesis – is a surgical method of bone stiffening for severe fractures with displacement.
- The Ilizarov apparatus is used for fractures with displacement.
recovery period
Rehabilitation therapists use the following techniques to restore function and anatomy to the injured limb:
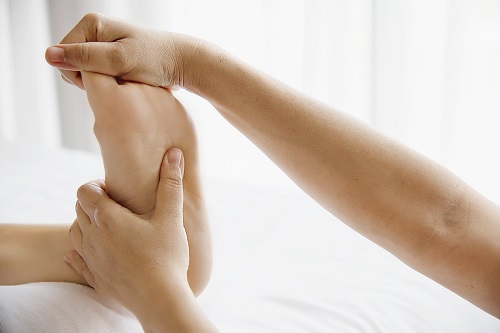
- Injection of various drugs into biologically active points of the foot with the help of needles.
- Therapeutic massage. Helps restore blood circulation and relieve pain.
- Physiotherapy.
- Wearing a splint for at least a year after the injury.
- Therapeutic exercises. A specialist will select a complex of exercises that will help you quickly return to a normal life and avoid limping.
- Tape application. Muscles and ligaments are fixed with special straps.
- Pilates, yoga – exercises help to relax, improve the flexibility of the ligaments and the mobility of the joints.
- Nutritional therapy. Prescribing foods to accelerate bone regeneration.
External foot pain
Human feet have a complex structure. This allows people to stand and move safely. Every day, the feet fulfill important functions: They help to maintain balance, push off from the ground and cushion movements. This ensures that shocks caused by contact with the ground are not transmitted to the spine and skull. This prevents damage to the brain and spinal cord. But even such a complex, perfect mechanism can fail. Overuse often leads to pain in the outer part of the foot. This affects people of all ages.
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the condition, diagnostic tests should only be recommended by the attending physician. A specialist should be consulted to make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes of pain in the foot on the outer lateral side
There are many known causes of foot pain, and each requires a specific therapeutic approach. Treatment should only be carried out by a specialist doctor after carrying out a series of examinations to determine the real cause of the foot pain on the outside. The main causes of this symptom include the following pathologies:
- Arthrosis;
- Contortion;
- Osteoporosis;
- Achilles tendinitis;
- heel spur;
- Morton's neuroma;
- Valgus deformity of the foot.
However, it is important to remember that there are also physiological causes of foot pain. This may include wearing uncomfortable footwear. Women are particularly susceptible to this factor. High heels and narrow toes can cause pain in the outer part of the foot. Once the feet are freed from uncomfortable footwear, this symptom disappears. In such cases, no treatment is required. However, if the feet are systematically exposed to uncomfortable footwear, the situation worsens and leads to joint deformation. Synovitis, arthritis, osteoarthritis, fasciitis and other diseases can result. Excessive physical exertion can also promote the development of these diseases.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of foot pain can only be made by a qualified doctor after conducting an examination and collecting all the necessary data. Diagnosis of foot pain from the outside includes the following methods:
| diagnostic procedure | Time |
|---|---|
| X-ray of the foot | 15-30 mins. |
| Ultrasound examination of the foot | 30 minutes |
| CT scan of the foot | 15 minutes |
| MRI of the foot | 20 minutes |
Each of these methods provides information about the bones, muscles, tendons, blood vessels and skin of the foot. The examination can be carried out in any medical institution that has the appropriate equipment. The costs for the individual diagnostic procedures vary. The most cost-effective examination is the ultrasound examination. Their price starts from 1,110 rubles. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are considered the most expensive. The cost of these procedures starts from 4,000 rubles. However, the accuracy of the data obtained fully justifies the costs.
Read more:- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- First metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot (metatarsophalangeal joint).
- Stages of hallux valgus.
- chalgus valgus.
- flatfoot μb.
- Deflection of the first toe.
- Cracked metatarsal.
- Shapar joint.
