With permanent damage (obesity, trauma, progressive osteoporosis), the fibrous ring of the disc thins and cavities form in it. Due to these weak points in the fibrous ring, the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc can move and even bulge.

- abdominal pain in women
- Abdominal pain in women: causes
- structure and location
- fracture of the hip bone
- Where are the lymph nodes located?
- Lymphadenopathy in viral and bacterial infections
- signs
- When to see a doctor
- This is what a CT scan of the brain looks like
- Evaluation of a CT scan of the brain
- Causes of lower back pain
- Physiological causes
- Visit school for free
- After you sign in
- Answers to popular questions
- If your pain is caused by a damaged frenulum lip
- what can be done
- Pain in the salivary gland
- side effects.
- Ceftriaxone and alcohol: tolerability
abdominal pain in women
Abdominal pain is the most common reason for women to see a doctor. This pain is a rather vague symptom and can have completely natural causes or be a consequence of various diseases.
The exact cause of abdominal pain in women can only be determined by a doctor.
In the vast majority of cases, the cause of abdominal pain is an inflammatory process that develops in the body of the beautiful half of humanity. The disease manifests itself differently depending on the individual characteristics and the stage of development of the disease. Painful discomfort can appear over time after previous surgeries or injuries.
In any case, a doctor should always be consulted. At the slightest suspicion of illness, an appointment with a specialist should be made.
Abdominal pain in women: causes
All causes of abdominal pain in women are divided by doctors into two groups:
The second group of causes of abdominal pain in women usually includes:
- Pain can occur with premature pathological detachment of the placenta, a threatened miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, after miscarriage and various gynecological operations;
- Wearing an intrauterine device as a contraceptive method;
- Diseases of the organs responsible for fertility: ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, endometritis, ovarian apoplexy, torsion of the ovarian cyst body;
- Pathologies of the urinary tract.
structure and location
The iliac crest is the inferior vastus. The shaft of the bone partially attaches to the hip joint, this symphysis forms the acetabulum or fossa, and another part of the shaft of the bone touches the massive sacrum.

During puberty, the hip bone comes into contact with the pubic bone and the buttocks, the trio ossifies and forms the pelvic bone. The shaft that extends upward is called the wing, and the surfaces of the hip bone space are called the crests. There are four bones in each bone formation:
- The more pronounced front upper leg;
- the slightly less pronounced lower frontal bone;
- the symmetrical posterior superior bone;
- And, as you can easily guess, the posterior mandible.
Near the right axis is the eminence of the lumbar spine. In contrast, the left axis forms a large ischial notch. The concave inner side of the wing is called the iliac fossa, and behind it is the articular surface of the hock. The outer part of the bone, on the other hand, is uneven because the gluteal muscles attach to it.

fracture of the hip bone
One of the causes of the pain in the characteristic area is a fracture. This is the result of abnormal compression of the bony structures caused by a direct blow. In this condition, there is extensive bleeding and a large blue hematoma on the skin. The musculoskeletal system is damaged and the muscles of the anterior peroneal wall are abnormally tight. Other symptoms of this characteristic disease are
- Sharp pain when trying to move leg;
- impairment of right or left leg function, depending on the location of the lesion;
- Severe swelling of the affected tissue, edema in the proper sense.

Since this structure is subject to systematic compression and can act directly on it, clinicians do not deny that fractures are common in patients of different age groups.
| age group | Common Causes | means of prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Young people | Fractures often occur in connection with the practice of sports. The more aggressive the sport, the greater the risk of such an injury. | These injuries cannot be prevented; they are situational. The only thing that can help is the use of protective gear. For example, special shorts have been developed for hockey players. These protect players' hips from bruises. |
If a fracture is suspected, it is not advisable to do anything at home. The patient urgently needs to be transported to the hospital lying on his back, placing a pillow 15-20 cm high under the knees for protection. If there is no dislocation, local anesthesia is given (needle with anesthetic in the affected area), a special splint is placed on the leg, and bed rest is recommended for the next 3-4 weeks. In case of displacement, general anesthesia and surgery will be performed.
Where are the lymph nodes located?
| part of the body | Where are you? |
| upper limbs | – under the armpits, – On the elbows. |
| Head | – around the ears, – Under the jaw. |
| thorax | – Around the trachea and bronchi, – near the sternum, – between the ribs. |
| Neck | – In the front part of the neck, both on the surface and in depth. |
| pool | – Near the sacrum, – hip bones. |
| lower limbs | – In the groin, both superficial and deep, – Below the knees. |
| abdominal cavity | – In the region of the liver, – stomach, – internal genital organs in women. |
Lymphadenitis occurs when infectious agents enter the lymph nodes. Inflammation usually occurs when pus-filled bacteria, such as streptococci or staph, invade the lymph nodes. But sometimes it is also caused by other microorganisms that are causative agents of certain diseases:
- Viruses – Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
- Bacteria – gonococci, tubercle bacilli, spirochetes, Francisella tularensis, plague bacilli and others.
Sometimes lymphadenitis is due to non-infectious causes. They can also be caused by autoimmune diseases or tumors.
Danger!!! Lymph node enlargement is not always associated with inflammation. The enlargement can be accompanied by an increase in immune cells, which ensure the destruction of the body's own cells.
Lymphadenopathy in viral and bacterial infections
In most cases, the lymph nodes enlarge against the background of infectious diseases. Lymphadenopathy is most commonly associated with acute respiratory disease caused by
- influenza and parainfluenza viruses;
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- coronaviruses;
- pneumococci;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- other viruses and bacteria.
signs
If a lymph node is swollen, but you don't have a fever, you don't have tenderness, and your general health hasn't deteriorated, you're fine—it's just that that lymph node is more active than others. He moves away from him.
It's worse if you have lymphadenopathy and feel faint, have pain in your ears, throat, or head, and have a fever. Report to your family doctor. If the cause of your fever is a cold or flu, he or she can help you treat it or refer you to another specialist. For example, go to the dentist if tooth decay is the problem. Eliminate the underlying condition and your lymph nodes will return to normal.
However, there are cases when inflamed lymph nodes can cause serious discomfort and even be life-threatening. In this case, you should be alarmed and go to the doctor.
When to see a doctor
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is called lymphadenitis. It can be acute or chronic. It can be caused by specific or non-specific pathogens. The symptoms depend on it. For example, the nodules can become inflamed after a cold or flu. If so, a doctor should be consulted if the following symptoms occur:
Symptoms of acute lymphadenitis are as follows:
- Lymphadenopathy (enlarged nodes - one or more). The enlarged nodules may be palpable as mobile, round masses.
- Painful pressing of the enlarged nodes with fingers.
- Decreased or complete loss of appetite.
- Fever (sometimes up to 39-40 degrees).
The symptoms described above are characteristic of the first two phases of lymphadenitis - the cathartic and serous phases. In the first phase, the inflammation is confined to the nodule itself and the symptoms are less severe. In the serous phase, the inflammation can spread to nearby tissues and vessels. The symptoms then quickly escalate. Regardless of the severity of your symptoms, you should make an appointment to see your doctor.
This is what a CT scan of the brain looks like
A CT scan through the bone window shows the structure of the cranial vault, the base of the skull, and the anterior part of the skull. The frontal sinuses can be seen in the frontal area. The vestibular, lambdoidal, and occipitotemporal sutures can be seen on the arch bones. The bony parts of the temporal bones are clearly visible, the area of the Turkish saddle with clear contours.
The eyeballs are cone-shaped on the CT scan, with the tips pointing backwards. In the craniofacial area, the nasal bones, labyrinth cells and maxillary sinuses are identified.
The window scan of the brain uses an area that is close to the density of brain structures. Axial scans show:
- cerebral cortex;
- III, IV, lateral ventricles;
- frontal horn;
- Islet;
- ventricular opening;
- vascular plexuses;
- diencephalon; etc.
- cisterns of the brain;
- vault;
- cerebellum;
- brainstem;
- Pituitary and hypothalamus (with contrast medium).
A frontal projection is suitable for imaging:
Axial slices allow the horizontal dimensions of the mass to be determined, while sagittal and frontal projections show the vertical dimensions.
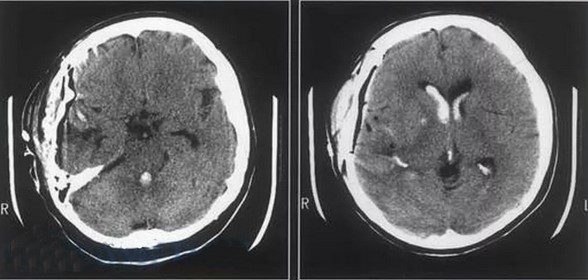
Sliced CT shows changes in shape, size of morphological compartments, and structural abnormalities of the brain.
Evaluation of a CT scan of the brain
The radiologist analyzes the images obtained. In the case of a repeat CT examination, it is important to show the doctor the results of the previous examinations. The doctor will analyze the dynamics of the pathological process and evaluate the changes that have occurred.
In the description, the location, size and shape of the morphological formations of the brain are determined. If there are pathological changes, then the nature of the process, the location of the abnormal area and the degree of damage to the brain structures are determined. The specialist analyzes the images captured in Bone and Brain modes. Axial, sagittal and frontal projections must be evaluated to get a complete picture.
The radiologist also considers possible artefacts in his conclusions. Defects in medical devices must be noted in the examination report. Accidentally moving the patient during the procedure makes interpretation of the results difficult. At the edge of the media, motion artifacts can be mistaken for signs of a pathological process.
The preparation of the medical report takes up to 2 hours. The results are reproduced on a CD and given to the patient.
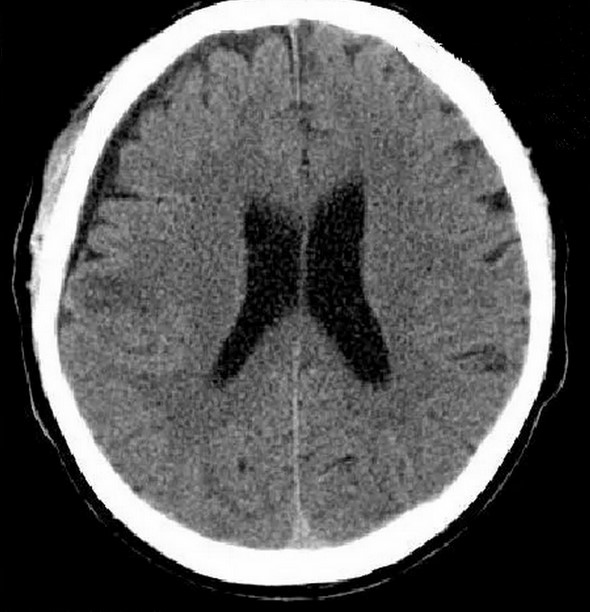
Consequences of a brain injury in a CT scan
The Magnet Medical clinic offers a second opinion service, in which two medical specialists examine the images produced. The radiologists reach their conclusions independently, which significantly reduces the risk of medical error.
To book an appointment for a brain CT scan, call +7 (812) 407-32-31 or visit the clinic's website.
Causes of lower back pain
Back pain is such a non-specific symptom that it can be caused by many different factors. Depending on how intense and severe the low back pain is, whether it's constant or recurring, whether it's primary or secondary, there may be other causes that trigger it:
- osteomyelitis;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- deformed spondylosis;
- growth disorders – scoliosis;
- Infectious lesions of intervertebral discs and vertebrae (epidural abscess, spinal tuberculosis, brucellosis);
- Metabolic bone diseases - osteomalacia, osteoporosis;
- Primary and metastatic neoplasms of the spinal cord, vertebrae and retroperitoneal space;
- Non-infectious inflammatory diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis;
- kidney tumors;
- Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta and its branches.
- spondyloarthritis;
- hip joint abnormalities;
- Epidural inflammation of the spine;
- Lumbar disc protrusion;
- osteochondrosis of the spine;
- Acute disc prolapse;
- Intestinal obstruction, atypical course of acute appendicitis;
- urolithiasis;
- Acute dislocations, vertebral fractures;
- lumbago, sciatica;
- Acute circulatory disorders of the spine - stroke;
- Acute pyelonephritis.
Irritating pains caused by certain internal diseases:
- Diseases of the abdominal organs. In women – inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages, endometriosis, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc.) In men – prostatitis, prostate cancer;
- Diseases of the stomach, pancreas, duodenum, gallbladder;
- Intestinal diseases - diverticulitis, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, intestinal tumors;
- Kidney diseases - renal colic, kidney stones;
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm with disease.
Physiological causes
Lower back pain can occur when:
- you are overweight;
- Additional risks for women;
- you are pregnant or have recently given birth;
- you spend a lot of time in the car or on the computer;
- Do mostly a sedentary (office worker) or standing job (salesperson, waiter, street performer, surgeon);
- Dynamic physical work with sudden changes in posture (especially if your job involves great physical exertion);
- Excessive exertion at the gym or health club. Be especially careful if you have just started exercising;
- They are engaged in gardening;
- You are in the postmenopausal phase, which favors the development of osteoporosis.
Visit school for free
After you sign in



Answers to popular questions
Can't find the answer to your question? Write to us on your social networks
During the introductory lesson, our advisor will introduce you to the online English course, explain the platform and help you determine your level and goals. This course is free and lasts 30-40 minutes.
You can attend school whenever you want. All you have to do is log in and sign up for a lesson.
All you need is a computer or phone with a microphone, camera and internet access. Whether you are in Moscow, Kazan, Novosibirsk or Bali, online English lessons are just a click away.
There's nothing wrong with that, it happens! Students have the option to cancel classes up to 8 hours before the scheduled time without forfeiting payment. This allows you to reschedule your lesson to a more convenient time, allowing the teacher to adjust your schedule.
You can learn English at your own pace. We will find a suitable date for you and help you to postpone your appointment, take a break or adjust your program at any time.
The introductory session lasts 30-40 minutes, while all other sessions of the adult English course last 50 minutes.
Leave an online application and record a short audio interview about your experience. We will contact you via email to inform you of the next steps. Don't worry, we'll first introduce you to our platform, and then a careers advisor will take on the role of the student in your first lesson. Once you have successfully completed the selection process, you can open your timetable and start teaching immediately.
If your pain is caused by a damaged frenulum lip
- Oral diseases - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- Improper use of oral hygiene products - toothpaste, toothbrush, mouthwash;
- allergies caused by medication.
Frenitis can also be caused by trauma to the frenulum from brushing teeth, eating (food that is too hot or cold), speaking too loudly, biting your tongue too hard, and careless use of utensils.
There may also be a physiological reason why the frenulum hurts under the tongue. If the frenulum is born too short, the chances of damaging it greatly increase, and you may even have trouble eating.
what can be done
If the frenulum under the tongue hurts, a visit to the dentist is essential. The doctor will examine the lesions and recommend treatment. At home, you can rinse your mouth to relieve pain, especially if you cannot immediately consult a specialist:
- A solution of baking soda (a teaspoon per glass of cooled, boiled water);
- a decoction of chamomile or sage;
- Preparations: Stomatofit, Rotokan, Horophillipt.
It is also advisable to treat the lip frenulum under the tongue with iodinol or apply cotton wool soaked in sea buckthorn oil. This can only happen when one knows for sure that the cause of the pain under the tongue is an inflamed tongue frenulum.
Pain in the salivary gland
If a person experiences pain on both sides of the tongue, it may be due to inflammation of the salivary glands. It is caused by:
- Complications of another disease (tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, anemia, avitaminosis, dental problems);
- insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of the flow of saliva by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms that indicate salivary gland inflammation are:
- Dry mouth - there seems to be a constant lack of saliva;
- pain that occurs not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- redness of the mucous membrane, a lump or swelling under the tongue;
- An unpleasant taste.
If these symptoms appear, you should see your dentist immediately and seek treatment. Otherwise, an abscess may form or a chronic condition may develop.
If you have a problem similar to the one described in this article, please contact our specialists. Do not diagnose the problem yourself!
Why you should call us now:
side effects.
Ceftriaxone has undergone numerous clinical studies, which have identified the most common side effects:
- Blood count changes: leukopenia, eosinophilia and thrombocytopenia
- rash
- Elevated liver enzymes
- diarrhea
The safety of ceftriaxone in pregnant women has not been established. Preclinical studies have not shown any teratogenic or toxic effects on embryo-foetal development. The use of the drug in pregnant women is acceptable only in the case of strict indications and in severe conditions, when other measures are ineffective. It is advisable not to prescribe the drug before the 10th-12th week, when the arrangement of the most important organs and systems takes place. During this period, ceftriaxone is only prescribed if the mother's life is in danger.
Ceftriaxone and alcohol: tolerability
Treatment with any antibiotic entails limitations, including the consumption of alcoholic beverages. It is advisable to avoid alcohol when taking antibiotics. This protects the patient from side effects and makes the therapy as effective as possible.
Antibiotics are prescribed for diseases that require rapid and even distribution of the drug in the bloodstream for maximum treatment effectiveness.
Replacing them with oral medicines (tablets, capsules) is not entirely equivalent; even identical substances have different effects on the body.
Let's list the group of analogues of ceftriaxone in tablets or capsules:
- Cephalexin - a first-generation cephalosporin.
- Zinnate (active ingredient cefuroxime) is a second-generation cephalosporin.
- Suprax and Pancef (active ingredient cefixime), third-generation cephalosporins.
Only the doctor can decide whether to replace cefatriaxone.
Let's compare two injectable cephalosporins: cefazolin or ceftriaxone. Which one is better?
Cefazolin belongs to the first generation and has a narrow spectrum of antimicrobial activity (gram-positive cocci). Therefore, there are fewer indications for the treatment of diseases: prophylaxis during surgical interventions, skin and soft tissue infections. The frequency of administration is 3-4 times a day.
Ceftriaxone, as a representative of the third generation, has a wide spectrum of activity against gram-negative flora, is resistant to bacterial enzymes and is used to treat severe and mixed infections. It is administered once a day and maintains the bactericidal concentration in the body over a long period of time.
The advantages of ceftriaxone are its effectiveness, its wide range of indications, its ease of use and its good safety profile.
Read more:- Which legs are considered long in women?.
- cruciate ligament of the foot latin.
- parts of the human leg.
- What is the part of the leg below the thigh called?.
- The parts of the human leg are named.
- Photo of the right leg.
- The pubic ligament where it is located Photo.
- Ligaments of the human leg.
