Physical overload overloads the tendons and ligaments that stabilize the joint. The swelling cuts off the blood supply, and when mechanical damage to the cartilage is added, there is a gradual breakdown. The periarticular tissue and the intra-articular capsule become inflamed - the properties of the synovial fluid change, so that osteoarthritis is not far away.
- Causes of injuries in soccer
- Types of injuries in soccer
- Anterior cruciate ligament injury in knee
- ankle injuries
- hip injury
- groin injuries
- meniscus tear
- Injury to the adductor muscle in the groin.
- Muscle injury in thigh area
- stretching in the knee area
- How is post-traumatic arthritis treated?
- When conservative therapy is ineffective
- What do footballers suffer from?
- First aid
- Immediate medical care
- Injuries in soccer players. Treatment and prevention of stress fractures
- testimonials
- How to treat abrasions and wounds?
- What should I do if my child has a severe bruise?
- Ligament injuries
- Medical treatment of ankle injuries
Causes of injuries in soccer
There is a perception that injuries in soccer are due to aggressive play. In fact, however, there are many more causes of injuries in this sport. The most likely causes include:
- Violation of the training regime
- eating disorder
- sleep disorders
- uncomfortable sports shoes
- Violation of sports ethics
- bad playing surface
- bad weather conditions
Types of injuries in soccer
Soccer injuries are characterized by a limited list of injuries that are most common among athletes. The most common injuries involve the legs, with goalkeeper injuries being associated with hand injuries.
Anterior cruciate ligament injury in knee
Injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee are among the most common injuries in soccer. It is a tear or dislocation of the ligament that is responsible for fixing the knee joint.
- Crunching or cracking in the knee
- instability of the knee
- Severe, stabbing pains
- swelling of the joint
- restriction of freedom of movement
ankle injuries
Ankle injuries are the second most common accidental injury in soccer. The most common accidental injuries in soccer are sprains and strains of the ankle.
- Acute pain after injury
- Rapid swelling of the joint
- Crunching at the time of injury
- restriction of mobility
- bruises
- Numbness in toes
- Difficulty in axially loading the injured limb
hip injury
A hip injury can occur when the inside of the foot hits the ball of the foot. In this case, the joint capsule is damaged. This injury must be treated appropriately, otherwise it can become chronic.
groin injuries
Soccer groin injuries are dislocations or tears of one or more of the five adductor muscles. The dislocation can be caused by moving the legs against a resistance. There are three degrees of severity of groin injuries.
- Pain in the groin when moving
- bleeding and swelling
- restriction of freedom of movement
- inability to bring the legs together
- pressure at the injury site
meniscus tear
A meniscus injury in soccer is one of the most common. A meniscus tear occurs when the knee is twisted or hit directly. There are four main types of injuries.
Injury to the adductor muscle in the groin.
This is a tear, or in the worst cases, a tear in one of the adductor muscles. These muscles are responsible for bringing the legs together. A minor injury may not be noticeable when walking and may be accompanied by discomfort in the inner thigh. More severe injuries can cause acute pain, discomfort even when walking, bruising, and swelling.
SV: It is indeed a very common injury. Football is developing, the demands on players are increasing, the game has become more dynamic. The body reacts to these stresses and this leads to muscle fiber tears. These injuries are less common among amateurs because they are under less stress. If you suffer such an injury, you should see a doctor, and in some cases, surgery may be required.
Who. In January this year, two Real Madrid players - Toni Kroos and Keylor Navas - were affected by this problem at the same time. Lokomotiv defender Maciej Rybusi was among the RPL players in early September.
Muscle injury in thigh area
Another common injury that does not only occur in football players. These muscles are responsible for bending the leg at the knee and extending the leg at the hip joint. The injury is accompanied by severe pain and sometimes redness. A minor injury can be treated without medical attention, while a serious injury will require medication. In laypersons, such injuries sometimes occur because they do not warm up adequately before a sudden increase in exertion.
Who. Recently, Barcelona midfielder Ousmane Dembele injured the back of his thigh in a Champions League game. Similarly, Real Madrid midfielder Marc Asensio sustained a front thigh injury late December last year. All Russian football fans probably still remember how Alan Dzagoev left the field in the opening match of the 2018 World Cup because of a hamstring injury.
UW: These are probably the most common injuries suffered by soccer players. These injuries are accompanied by muscle spasms. A tear can occur, for example, when a player's leg slips on a bad pitch. On average, such injuries take 3-4 weeks to heal.
stretching in the knee area
- Tight tear/splint in the knee area
- Unstable knee joint/strain
- Sharp, sudden pain that comes on immediately
- Severe swelling
- Stiffness/inability to fully straighten the leg
Statistically, an anterior cruciate ligament tear is three times more likely to be diagnosed in women than in men. This has not been scientifically proven, but is believed to be due to anatomy.
The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four ligaments that stabilize the knee and prevent it from moving freely. The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from sliding forward under the femur. The posterior cruciate ligament has the same function, just in reverse. Together they play an important role for the knee, especially in contact sports.
A cruciate ligament tear in the knee can be caused by
- a sudden movement (when jumping or landing);
- a direct blow to the knee;
- a fall on the knee while running (especially if the athlete is pushed).
How is post-traumatic arthritis treated?
Any type of injury can be a trigger for the development of joint stiffness. It's not just broken bones, meniscus injuries or tendon tears. Bruises, especially those with accumulations of blood in the joint cavity, dislocations and micro-injuries that are not visible to the naked eye can also be dangerous. Professional athletes are affected by injuries more often than others.
In this category, ankles and knees are most commonly affected. Hip and shoulder joints and wrists are affected less frequently. Osteoarthritis of the knee or other joint is usually treated in several steps:
- analgesics to relieve acute pain;
- anti-inflammatory drugs – inflammation is shown by swelling around the joint area;
- full restoration of the cartilage tissue, if the clinical situation allows, or, in complicated cases, partial arrest of the degenerative process;
- Physiotherapy such as massage, electrophoresis, acupuncture, etc. are recommended in the non-acute phase.
The earlier the athlete seeks treatment, the better the chances that he will be able to pursue his favorite pastime.
During training, joints and tendons are subject to wear and tear. This process cannot be stopped, but it is possible to protect the joints from further wear and tear and inflammation! How to properly organize sports nutrition?
When conservative therapy is ineffective
If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical treatment is necessary. In many cases, surgery can be avoided by increasing the amount of synovial fluid in the joints - with the help of an endoprosthesis. In the second and third stages of post-traumatic arthritis, a single intra-articular injection of Noltrex per year is sufficient to relieve pain and restore mobility.
In sports traumatology, prophylactic treatment is also carried out to maintain optimal joint health. Depending on the location of the injured joint, the athletes receive several doses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and angioprotectors per year. 2 to 3 times a year it is advisable to undergo massage therapy and physical therapy of the injured area.
Even if you already have joint problems, this is not a judgement. Don't be in a hurry to give up the sport unless your orthopedist insists. Thanks to modern techniques and innovative treatment approaches, in most cases osteoarthritis can be stopped and controlled, and you can continue to do what you love.
What do footballers suffer from?

Football never fails its players, even when they are not on the pitch. Most of the illnesses that most commonly affect footballers are related to their injuries in one way or another. The following diseases are included in this list:
- Inflammation of the joints (arthritis) and the joint capsule (bursitis).
- Inflammatory processes resulting from injuries and overuse of tendons (tendinitis) and ligaments (ligamentitis).
- Inflammatory diseases of the periosteum (periostitis).
- Inflammation of the muscles (myositis).
- Inflammation of the blood vessels: vasculitis and its variant phlebitis (inflammation of the vein wall).
- Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (Goff's disease).
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. The likelihood of developing these abnormalities increases in response to traumatic brain injury.

- MartinPalermo. The Villarreal player ran off the field after scoring a goal in 2001 and grabbed the fence. The fans rushed to congratulate him and he fell off the fence on Palermo. The fall from the fence cost him a fractured fibula and tibia and six months in hospital.
- Peter Biaxangzuala. The India international, unable to contain his emotions after a successful game, did a somersault and fell on his head. His cheering Indian teammates collapsed on top of him, unaware that their teammate had fractured his spine in the fall. The footballer died in hospital.
- Paulo Diogo. The 2004 Servet FC player ran towards the fans after scoring a goal. Diogo jumped the fence and lost two fingers and ripped off his wedding ring.
Soccer is a difficult game, but a fun and extremely addicting game. On the first day of the 2018 FIFA World Cup, MedAboutMe wishes the Russian national team a successful game and no injuries to all players.
First aid
The primary goal of first aid is to immobilize the injured joint and reduce the resulting swelling. The so-called RICE technique is used for this, an acronym for four words: rest, cold/ice, compression and elevation.
Let's go through each technique briefly:
- Quiet. Avoid putting any stress on the joint, not only to relieve the pain but also to prevent it from getting worse with stress. This means either using crutches or waiting for the emergency services to arrive for extensive transport to the clinic.
- cold therapy. Ice or cold packs should be placed on the injury for about 15 minutes. Cold therapy can be repeated every 2 hours for 15 minutes. This will relieve some of the pain, reduce swelling, and slightly improve blood flow to the injured area. In futsal, sports freezing is usually used in such cases, which is the most effective method of cooling the injury.
- compression. To limit bleeding and reduce swelling, special ankle bandages or sports tapes are used to keep the joint in the correct position.
- Elevate. Once the athlete is supine, it is best to elevate the leg to allow gravity to draw fluid from the injury site, which should reduce swelling. If the leg is fixed over the body in a supine or seated position, the player is relieved and the leg cannot fully descend.
Immediate medical care
The next step is for the paramedics to determine the extent of the injury and take action. In severe cases, when a complete rupture of the ligament is diagnosed, surgery is required. In simpler cases, various repair gels and dressings are used. Complete rest and a rehabilitation measure to restore the plasticity of the joint are mandatory.
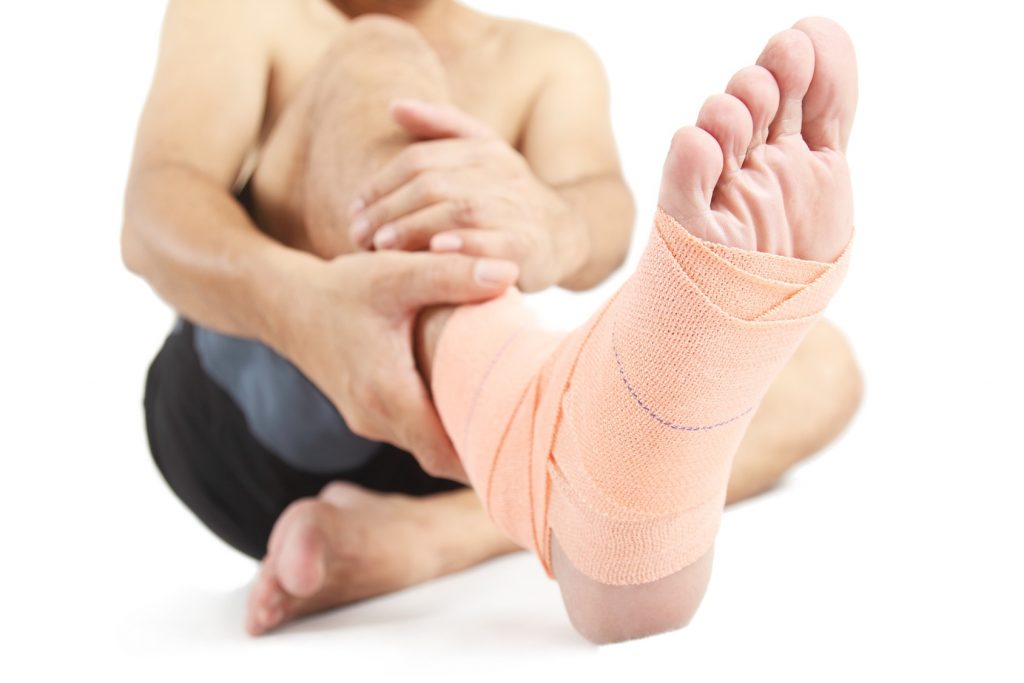
Injuries in soccer players. treatment and prevention
stress fractures
Statistically, soccer is the sport with the most trauma. This is due to the frequent collisions of players at high speed, rotational movements of the lower limbs while standing, training on hard (artificial) ground, and the high emotional intensity of the game.
Injuries in soccer players can be caused by a sudden impact that exceeds the physiological limit of tissue strength; in this case, ligament tears and fractures occur, which are treated in specialized hospitals, often using surgical techniques.
However, injuries often occur among athletes who are subjected to enormous loads that gradually lead to the inability to train, let alone play.
These pathologies include the so-called stress fractures. They occur with physical overloads of the same kind, when the remodeling of the bone bars occurs under excessive and constant stress. In other words, they are micro-level bone fractures that initially affect only some structural and functional units of the bone, which are then allowed to heal with the formation of callus. However, the overload continues and new microfractures develop in the same area and again connective tissue bridges are formed to heal the area.
This creates zones of pathological bone remodeling which, if overloaded further, lead to a real fracture. For this reason, these fractures are referred to as 'stress fractures' as they occur when the bone is subjected to an impact load. Statistics show that the frequency of these injuries is high: they account for about 10 % of all sports injuries, with 95 % involving the tibia and foot.
In soccer players, the 5th metatarsal is the most stressed bone during a sudden stop after a fast run with a pivot point on the outside of the foot. (Fig. 1) Other parts of the skeleton that often undergo pathological changes in soccer players are the scapula, heel and tibia.
testimonials
A big thank you to Dr. Fancello for restoring my physical health and belief in victory. He is a wonderful doctor who helped us with our joint problems. Regina has been dancing for five years, pulled feet, pulled heels, injuries……. She had constant injuries from knee to foot. After visiting the osteopath, we felt a significant improvement. The osteopath worked with the spine and pelvic bones, balancing the body. Now injuries are a thing of the past! Thanks to Jean we have achieved many victories in dance competitions and tournaments.
A big thank you to Dr. Fancello! My son had severe hip pain and after exercise the pain got worse. Michael is 16 years old and had no serious injuries. We didn't know what to do. Friends of friends told us about Fansello, he came highly recommended. We made an appointment with him and after the first session the pain was gone! Thank you very much. (My son had a pinched nerve which the doctor fixed in the first session). Sincerely Tumanov Mikhail.
A big thank you to Dr. Fansello, for restored physical health and belief in victory. After tearing my ankle ligaments, I thought I could forget about the upcoming tournament. Recovery has always taken a long time, but after the visit to Fansello it happened very quickly. He not only worked on my leg but also solved my back pain which is very important for me! Thank you for all the support, I feel great! Thank you for your attention and your caring and kind hands.
A big thank you to Dr. Fancello. I've had a lot of injuries just like any other athlete. During my sporting career I had many injuries, sprains, torn tendons and dislocations. I am a performance dancer. A year ago I met the osteopath Fancello and I haven't had any injuries since! The doctor is great! First of all, he relieved my body of tension and cramps and got all my organs working again. He repaired my nervous system and taught me how to deal with physical and mental stress. How nice that nowadays there are still doctors like Dr. Fancello gives. Now just the awards!!! I wish I had had the opportunity to see a really first class specialist in Moscow sooner. A big thank you to Jean Fancello and the Ostmed Clinic
How to treat abrasions and wounds?
- The first rule with open wounds is cleaning. Wash the wound of any visible dirt with clean, running water.
- Then treat the wound with an antiseptic solution (e.g. Octanisept). Do not use alcohol-based products on the wound surface!
- If the bleeding is light, it will stop on its own within a few minutes. Cover the wound with sterile, self-adhesive material.
- If you need to stop the bleeding, apply a pressure bandage and apply cold.

In case of heavy bleeding, you should seek professional medical help!
What should I do if my child has a severe bruise?
- First, the injured player must be removed from the game immediately.
- Watch for open sores, joint mobility, and a crunching sound when you push and move.
Elevate the injured body part. - Apply cold (e.g. wrap a bag of frozen vegetables in a towel), use a mesh to fix.
If there is severe swelling and hematoma at the site of the bruise, consult a doctor!
Ligament injuries
These injuries can vary in severity: strains or tears of individual ligaments, tears of about half of the fibers, complete detachment of the ligament from its attachment point.
The injured person always complains of severe pain (only the intensity of the pain varies). He may have difficulty putting weight on the leg or moving, or even be unable to take a few steps.
The joint may be slightly swollen and change shape. The swelling may be slightly larger on the injured leg. If blood vessels have been injured, bruising can occur.
The joint can sometimes creak during movement.
When the ligaments are badly damaged, the bones can move, which can lead to dislocations or subluxations.
Medical treatment of ankle injuries
Don't try to straighten a sprained ankle. The injured leg should be immobilized, preferably with a splint.
If an open wound is present, it should be carefully treated with hydrogen peroxide, or at least clean water, and covered with a bandage.
If possible, a cold compress should be placed on the wound area. After that, you should always consult a doctor.
The traumatologist will examine the injury and ask questions such as: B. the situation in which the injury occurred.
The next step is to refer the patient for an X-ray examination. In the rare cases where the X-rays are not conclusive enough, an MRI, ultrasound or CT scan is ordered to clarify the diagnosis.
In very severe cases, an arthroscopic examination may be necessary. In this case, the doctor can eliminate the problem directly during the diagnosis.
Depending on the diagnosis, individual treatment is prescribed. In the event of a ligament tear, the joint is immobilized with a firm bandage.
In the case of hemarthrosis, the joint must be punctured and the blood removed. Dislocations should be treated with a plaster cast.
Displaced fractures can be repaired surgically, followed by traction and splinting.
In the recovery period, physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy are recommended.
Read more:- Treatment of torn ligaments in the ankle.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- Femoral collateral ligament.
- How to distinguish a fracture from an ankle sprain.
- The child walks with feet wide apart.
- How do you treat a sprained ankle?.
- Sprained ligaments in the metatarsal area.
- Where Perseus pulled from the stadium into the water.
