Discomfort and discomfort below the knee accounts for up to 30 % of complaints related to musculoskeletal disorders. However, these complaints do not always occur in older people or competitive athletes. Pain in the back of the knee can occur in all patients, since the causes of this symptom are different. If you experience discomfort in the lower limbs, you should seek medical help. Timely diagnosis is the key to effective treatment and a speedy recovery. Treatment on your own or with folk remedies can threaten your health and lead to such serious consequences as the progression of inflammation.
- lymphostasis
- causes
- Structure of the human knee joint
- Human elbow joint structure
- Kegel exercises for prostate adenoma – for men
- Yoga for prostate adenoma and prostatitis
- Section menu
- Basic Functions
- Temporomandibular joint diseases and their causes
- Causes of pain below the knee
- diagnosis
- Which doctor treats pain below the knee?
- Causes of left back pain
- varieties
- clinical picture
- How the diagnosis is made
- In the spotlight
- Why and how
- Diagnosis of tendinopathy
- Treatment
lymphostasis
Lymphatic flow is as important to the body as the blood system. Therefore, any anomaly in the structure of the lymphatic system is immediately recognized by visible external symptoms. These include lymphatic congestion or lymphedema, which is associated with impaired drainage of the lymph from the internal organs or limbs. The result is noticeable swelling and darkening of the skin where lymphatic fluid accumulates, which can only be resolved by visiting a qualified medical specialist. Around 10 million people are currently affected by lymphatic congestion, especially women who suffer from lymphatic congestion for physiological and hormonal reasons.
Depending on the cause of the lymphedema, a distinction is made:
Congenital pathology develops against the background of abnormalities in the formation of the lymphatic system during intrauterine development. In rare cases, a hereditary factor can influence lymph flow abnormalities. The incidence of primary lymphedema is about 6 % of all patients with this disease.
Acquired lymphedema is caused by unfavorable external factors. The first symptoms often appear in childhood and adolescence and later worsen during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to the hormonal changes in the body during puberty and pregnancy. Sudden progression of lymphedema can occur after pregnancy or major trauma.
causes
In most cases, the development of lymphoma is caused by the presence of the following diseases
- Infectious diseases that cause inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- Chronic venous insufficiency syndrome with thrombophlebitis and varicose veins;
- lymph node lesions and ductal stenosis;
- trauma and burns affecting the subcutaneous cell layer;
- cancers treated with radiation therapy;
- tumors in soft tissue;
- Penetration and growth of parasites in the structure of the lymphatic system;
- Diseases of the heart and kidneys that have caused permanent tissue swelling.

Exposure to one or more of these factors, combined with the anatomical features of the patient's body, leads to impaired conductivity and contractility of the lymphatic vessels. They lose their ability to circulate lymph throughout the body, causing congestion. This condition is particularly dangerous in the lower limbs, where the lymph fluid enters in large quantities under its own weight but is unable to travel upward through the contractile vessels.
Proteins, mucopolysaccharides and other organic substances are released from the lymph with prolonged congestion. These impregnate the vessel walls and disrupt their natural structure. Connective tissue grows rapidly inside the blood vessels, narrowing their lumen and impeding the flow of lymph in the body.
Structure of the human knee joint
The knee is a complex and large joint in the human musculoskeletal system. It allows movement of the lower limbs in relation to the hips and supports body weight. Movement of the knee joint is essential for everyday activities such as walking, running, sitting and standing.
The knee is a modified joint, a type of synovial joint, made up of three functional parts: the patellar (patellofemoral) joint, which includes the kneecap (patella) and is located at the front of the thigh, and the medial and lateral tibial joints, which connect the femur connect to the shin. The knee also has a cartilage pad, the meniscus, which acts as a shock absorber inside the knee. In addition to the joint capsule and ligaments that support the knee, there are also some important structures that surround the knee and help soften the joint and protect it from friction. These are small 'sacs' of synovial fluid called bursae.
Human elbow joint structure
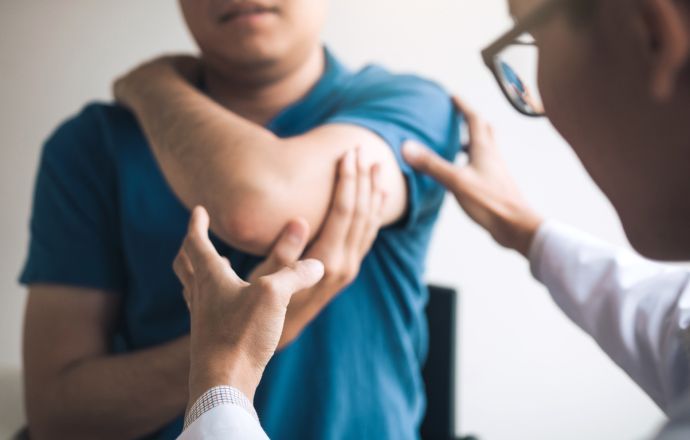
The elbow joint is a joint formed between the distal end of the humerus and the proximal end of the forearm. Like all other joints, the structure of the elbow consists of a smooth layer of cartilage. There is also a joint capsule that surrounds the joint and provides strength and smooth sliding.
The fluid produced by the synovial membrane of the joint capsule fills the empty space between the bones and lubricates the joint, reducing friction and wear. The extensive network of ligaments surrounding the joint capsule help keep the elbow stable and withstand mechanical stress. There is also a ring-shaped band that runs from the elbow bone around the head and holds the bones of the forearm together. These ligaments are responsible for the movement and extension of the elbow and protect it from sprains and strains.
Kegel exercises for prostate adenoma – for men
Gymnastics has been successfully used to treat prostate adenomas, prostatitis, hemorrhoids and erectile dysfunction.
- Alternate pressing and relaxing the buttocks at a fast pace; during pressing, the rectus and pelvic floor muscles should be maximally strained; you'll have the most impact if you do this while sitting in a squat position, but you can also start standing or sitting in a chair.
- Do the same thing, but tense for 10 seconds, then relax for 4 seconds.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees, place your feet together and alternately pull your knees apart and together.
Begin with 10 repetitions of each movement group in 4 approaches per day.
Yoga for prostate adenoma and prostatitis
Start with proper breathing. Focus on your stomach and breathe slowly using your diaphragm on a count basis: 4 for inhale, 4 for dwell, 4 for exhale. As you inhale and exhale, contract your pelvic muscles like a Kegel complex, and as you exhale, relax. After a few minutes of breathing, you can begin the asanas:
- Cobra Pose - lying on your stomach, place your hands and toes on the floor, raise your torso, stay standing for as long as possible;
- Plow Pose – roll onto your back, straighten your legs and pelvis, try to put your feet behind your head;
- Sit on your back in a chair, raise your upper body slightly and make a full circle with your pelvis as you inhale and exhale. Repeat the exercise 5 times in each direction.


If your body isn't very agile, don't try to build up a lot of tension right away, but gradually increase the tempo. Accurate execution and regularity are more important here.
The gymnastics can be performed alone or in combination with other effective techniques that you can learn at Dr. AcNer received.
Make an appointment in person, by phone or online. Our specialists can help improve a man's state of health, and in many cases even cure him completely.
Section menu
Basic Functions
Arthropods have many functions:

- moving the jaw forward and backward and in different directions;
- Chew;
- shape language.
If problems arise and there is displacement of the joint disc or degenerative damage, the joint can no longer fulfill its function. As a result, the sufferer loses the ability to chew and other skills. Due to temporomandibular joint dysfunction, the upper and lower rows of molars are gradually worn down. This changes the bite, affects the evenness of load distribution and causes incongruence of the articular surfaces (incongruence).
Temporomandibular joint diseases and their causes
- osteoarthritis. An inflammatory disease, infectious or non-infectious, in which the muscles, bursae, condyle, and intermediate joint structures become damaged. The pathology is the result of jaw trauma and systemic abnormalities in the body.
- osteoarthritis. Chronic pathology in which dystrophic changes develop in the joint. Caused by inflammatory complications, trauma and missing molars.
- tendonitis. In this condition, inflammation and damage to the tendon is diagnosed. Untreated arthritis or osteoarthritis is often the cause of this condition. Injuries and infections can also play a role in tendonitis.
- Synovitis of the temporomandibular joint. An inflammatory disease affecting the synovial membrane of the joint. As the disease progresses, abnormal fluid accumulates in the joint cavity, leading to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The disease develops as a complication of trauma and infectious diseases.
- contortions. Complete displacement of the condyle behind the tubercle as a result of trauma, inflammatory and degenerative processes, neuromuscular disorders or congenital anomalies of the nervous system.
- Subluxation (underluxation). In this case, we are dealing with an incomplete displacement of the head, provoked by trauma or an internal disorder. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomy, it is more often diagnosed in women.
The International Classification of Diseases ICD-10 divides joint diseases into 2 classes:

- XII – 'Diseases of the jaw and face';
- XIII – 'Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders'.
Causes of pain below the knee
The symptoms can be caused by damage to the cartilage or bone tissue, the periarticular capsule, tendons, ligaments and muscles. Treatment of back knee pain must always address the root causes, which include
- Injuries caused by heavy loads or impacts;
- inflammatory processes (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, synovitis, tendonitis);
- infectious lesions (psoriasis, some venereal diseases);
- kneecap dislocations;
- Congenital malformations of the joints.
Popliteal pain can occur reflexively and be caused by radiculopathy, arthrosis of the hip, or osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. The symptoms are also associated with benign (cysts) and malignant (cancer) tumours.
The doctors point out that the following patient groups are particularly susceptible to pulling, stabbing or aching pain in the back of the knee:
- People whose jobs are physically demanding or who have a sedentary lifestyle;
- people who are overweight;
- people suffering from endocrine disorders;
- elderly people;
- adolescents;
- pregnant women;
- People suffering from varicose veins.
In addition, many doctors say that some diseases that cause symptoms can be inherited.
diagnosis
The study to determine the cause of the ailments includes a number of instrumental and laboratory methods. When a patient suffers from pulling pain in the back of the knee, treatments such as the following may be recommended:
| diagnostic procedure | Time |
|---|---|
| Biochemical blood test | 10 mins |
| Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee joint | 30 minutes |
| Ultrasound examination of the knee joint | 30 minutes |
The examination to clarify the cause of the pain is often supplemented by an arthroscopic examination of the joint, a puncture examination of the knee. Differential diagnosis is always carried out taking into account the condition of the knees of both limbs.
Which doctor treats pain below the knee?
If you feel discomfort in your legs, make an appointment with a specialist. If you have no idea what could be causing your symptoms, consult your family doctor. Your doctor may also be able to help you:
Causes of left back pain
- Fracture or fracture of a vertebra as a result of trauma
- Curvature of the spine with pinched nerves
- Infection or inflammation of the spine
- Renal colic, other diseases of the kidneys or ureters
- inflammatory diseases of the heart or vessels
- Bone Marrow Diseases
- Malignant or benign tumors
- Inflammation of the lung tissue or the pleura
- Inflammation (colitis), infection or other diseases of the large intestine
If the left side of the lower back hurts, the kidneys should be examined. In renal colic, the pain occurs at waist level and extends to the abdominal region. It can also appear in the lower back and extend to the inner thighs.
varieties
The classification of left-sided back pain can be based on the type of symptom, the exact location of the discomfort, and the causes of this pathologic symptom. Doctors, as a rule, first consider the nature of the pain syndrome, since the initial diagnosis depends on this factor.
It occurs suddenly and lasts from a few hours to a few days. It is a constant discomfort that greatly affects the quality of life of the patient. A sharp, throbbing sensation may indicate renal colic, ureteral inflammation, or inflammatory diseases of the female genital tract. Dull pain is more common with spinal abnormalities. If a person complains of such a symptom when inhaling, the condition of the lungs and pleura should be checked.
If a patient suffers from constant back pain on the left side and the symptoms temporarily worsen, not only the spine, but also the internal organs should be examined. The spine, ribs, ligaments, muscles, urogenital system, digestive organs, heart or blood vessels can be involved in a pathological process. Upper pain syndrome associated with pain radiating to the shoulder, sternum, neck, or upper limbs can be a symptom of a heart attack.
clinical picture
The main symptom of a pinched sciatic nerve in the hip joint is a sharp, sharp pain in the lower back that radiates to the hip and buttocks. The intensity of the pain makes it impossible to move, bend, walk, and perform other leg movements.
In addition to the pain, patients also report the following symptoms:
- Limitation of the range of motion in the hip joint.
- Paresthesias – tingling and burning sensations in the affected area.
- Numbness at the site of impingement.
- In some cases, fever, chills, sweating, and weakness may also occur.
A recurring pain in the leg or back is called sciatica and is quite common in patients with sciatic nerve entrapment, especially when trying to change posture by standing or lying down, or when playing sports.
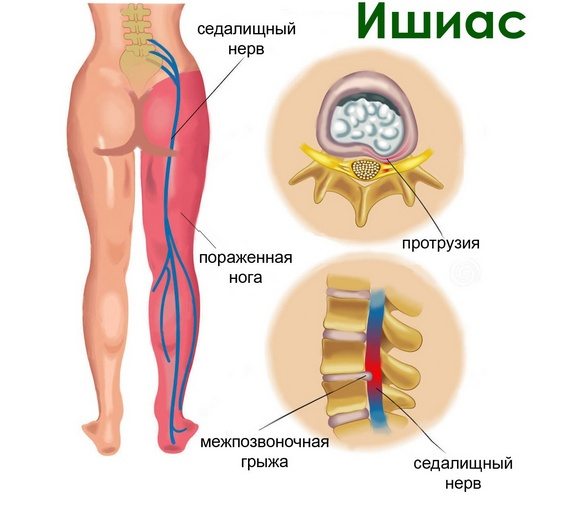
How the diagnosis is made
The patient's typical complaints of pain and retractions, paresthesias and accompanying symptoms usually make it easier to diagnose a pinched sciatic nerve. The doctor takes the medical history and orders imaging and laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine further treatment:
- CT scan, MRI of the spine and soft tissues;
- X-rays of the pelvic bones and spine;
- Ultrasound of the hip joint;
- electromyography;
- General and biochemical blood tests and general urinalysis.
In the spotlight
Our feet have a unique property - they are elastic. This property reduces the cushioning load on the joints of the lower limbs and the spine when running and walking. When the muscles and ligaments in the foot suddenly weaken, it becomes flat and can no longer perform its cushioning function. This is how flat feet develop.
– The difficulty is that the foot loses its original task of absorbing and absorbing the shock waves generated when walking or running, - says Sergiy Oleksiychik. — And because this does not happen, there is an enormous stress on the bones and musculoskeletal system: the ankles wear out faster, the spine twists, and the brain, tired of the microshocks, reacts with a headache.
Physiologically, the foot has two arches: longitudinal and transverse. The longitudinal arch resembles an arch - a kind of free space between the surface of the sole of the foot and the support plane: it is easy to recognize even for the layperson. The transverse arch, located in the middle part of the foot, cannot be seen with the naked eye. This requires an X-ray examination such as a CT or MRI scan.
When the musculoskeletal system is weak, the arches of the feet are lost and the normal shape of the foot is disturbed. If the foot is flattened in the longitudinal direction, slightly stretched and touches the surface not only with the outer edge, as is normal, but with almost the entire surface, one speaks of a longitudinal flatfoot. Toe deformity and the 'bone' at the base of the big toe indicate transverse flatfoot. If there is a flattening of the longitudinal and transverse arch at the same time, it is a combined flatfoot. This form is the most common.
When the arches of the feet are flattened, the cushioning function of the foot is impaired. This means that the force of impact when walking is now transmitted to the knee, hip joint and spine, which can lead to discomfort, pain and rapid fatigue when exerted. Solving this problem is not an easy task.
Why and how
Many factors contribute to the development of flat feet: genetic predisposition, obesity, lack of exercise, heavy physical work or work that requires you to stand for a long time. This should also be taken into account when choosing your future profession. The work of a hairdresser, salesman or waiter with flat feet is physically demanding, mainly because of the constant pain in the feet. Loadmasters, military personnel or lumberjacks face the same difficulties.
Inappropriate footwear is another important factor. Above all, lovers of shoes with high heels are more likely to suffer from a transverse flat foot. That's because high heels shift the load to the forefoot, which the muscles and ligaments can't handle. On the other hand, sneakers, moccasins, ballerinas and all shoes with a thin sole and no heel can cause flattening of the longitudinal arch. Therefore, the most reasonable solution is shoes with a wide and stable heel (up to 3-4 cm), without a pointed nose, not too loose, but not squeezing the foot. The sole should be flexible enough to cushion the impact on the foot when walking.
You should be particularly careful when choosing sports activities. Exercise strengthens muscles, improves blood circulation, and makes the body stronger, but not all physical activity is created equal.
– Any physical activity that does not put undue stress on the feet is good for flat feet, - believes Sergey Oleksiychik. — Physiotherapy, cycling, swimming, walking barefoot on uneven ground (on a special mat in winter, on sand or grass in summer) will help. A foot and shin massage may be recommended to strengthen the foot and shin muscles and relieve tension and pain. It reduces pain and swelling, tightens muscles and stimulates blood circulation. There is also a list of contraindications: weightlifting, athletics, Nordic walking and running. These activities should be exercised with extreme caution and best avoided altogether.
Diagnosis of tendinopathy
The orthopedist usually uses the following methods to diagnose tendinopathy:
- Orthopedic exam: The doctor may perform a physical exam to assess the level of pain, range of motion, and other signs of tendinopathy.
- X-ray examination of the joints: This diagnostic method uses X-rays to create images of the bones, which can be used to identify fractures, deformities and other abnormalities.
- Joint Ultrasound (USG): is a diagnostic method that uses sound waves to create images of tissues that help identify damage and inflammation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the joints: is a diagnostic technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues. This method can be used to detect damage, inflammation and other abnormalities.
- Computed tomography (CT) of the joints: This is a diagnostic method that uses X-rays to create detailed images of tissues. A CT scan can help identify abnormalities and damage that may accompany tendinopathy.
- Blood tests: Your doctor may recommend laboratory tests to determine the level of inflammation and to detect infections that may be contributing to tendinopathy.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of tendinopathy, but it is recommended in most mild cases:
- Rest until symptoms improve
- ice packs
- Wearing a compression bandage
- Elevation of the limb with the affected tendon at rest
- Pain relievers, particularly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
In more severe cases, shock wave therapy or even surgery may be needed.
Read more:- Shortening of the lower limbs.
- The muscles of the lower limbs are.
- Main joints of the lower limbs table.
- Structure of the human lower limbs with captions.
- Manufacture of lower limb prostheses.
- Muscles and fascia of the lower limbs.
- Ligament strain of the lower limbs.
- Where amputated limbs go.
