To prevent this, you should do stretching exercises, e.g. B. On a stair: Stand on the second rung of the stair with your heels hanging down, put your right heel down, and then stretch.

- Types of muscle injuries
- Injuries to the thigh muscles (thighs.
- Magnesium and leg cramps
- muscle cramps and magnesium
- prevention
- First aid measures for a calf sprain
- Prevention of muscle cramps
- Epileptical attack
- Application in children
- Mydocalm analogues
- specific treatment
- Causes of calf pain after running
- Wrong technique
- Poor quality of shoes
- Sudden interruptions in exercise
- specificity in girls
- Diagnosis of calf pain
- prevention
- Popular Questions
Types of muscle injuries
Treatment Types of muscle injuriesThey are mainly treated by sports doctors because they are among the most common sports injuries. However, patients come to our medical center with these problems, which are not necessarily related to sports activities. And if the diagnosis and treatment of open Muscle injuries While diagnosing and treating an open muscle injury is easier, treating a patient with a closed injury is more difficult.
- A contracture is a spasm, an excessive increase in muscle tone. The acute shortening of the muscle causes pain (with or without palpation) that is not clearly localized.
- Crepitus is a reversible change in a muscle caused by overuse.
- A sprain is an injury to certain muscle fibers that does not affect the connective tissue elements of the muscle in question. In this case, the pain occurs at the peak of physical activity and Damage to the muscle is clearly visible when palpated.
- A single torn muscle fiber is manifested by a sudden, stabbing, cramp-like pain. Only a limited number of muscle fibers are affected by the injury and the connective tissue is only slightly affected.
- Muscle tear – differs from the previous point in the number and extent of the injured components. In the case of this one muscle injury Both the connective tissue and the muscle tissue are damaged. The tear is manifested by severe pain and loss of motor function of the muscle.
- The complete tear or separation of the muscle is the most serious injury in this classification. The muscle tears transversely into two separate parts, which can sometimes be far apart due to spasms. Here the symptoms are striking: sharp, intense pain, sometimes with an audible noise immediately after the tear, as well as bruising, enlargement of the muscle, and inability to exert axial force on the limb.
Injuries to the thigh muscles (thighs.
Injury to the quadriceps muscle is a common complaint that patients with muscle injuries come to our clinic with. How does this injury occur? As a rule, this situation occurs during a fall, or more precisely, after a landing, when a person tries to straighten a leg bent at the knee. If the quadriceps muscle was previously stretched, it contracts quickly, resulting in a Damage to the hip muscle..
In up to 90 percent of cases, this muscle tears along the tendon and can also tear from its attachment to the shinbone. The tear pulls the bulk of the muscle upward, resulting in a sunken area above the knee.
The treatment of this Hamstring Injury consists in suturing the muscle fibers and tendons and immobilizing the limb with a cast splint for a month to ensure immobility.
Magnesium and leg cramps
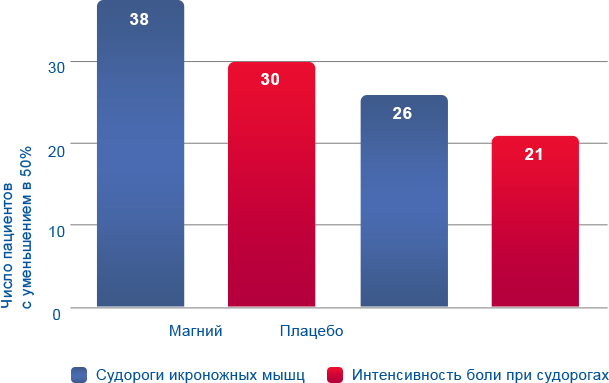
A magnesium deficiency can be compensated for by regular magnesium intake.
It is important that magnesium is taken over a longer period of time and in sufficient doses.
Magnesium can also be taken as a long-term therapy or treatment (4-6 weeks).
1 Rebrov VG, Gromova OA. Vitamins, macro and micronutrients. М., 2008. C. 960. 2. Torshin I, Gromova O. Magnesium: basic research and clinical practice. Nova Biomedical Publishers. NY, 2009:210. 3.Vidal Handbook. Pharmaceuticals 32 PHARMATheca № 8 – 2011 ACTUAL REVIEW of medicines in Russia: Handbook. М., 2010. C. 1488. 4. Torshin IY, Gromova OA Molecular mechanisms of magnesium action in the development of connective tissue dysplasia // RMZh. 2008. № 4. C. 203-09. 5. Torshin I.Yu., Gromova OA. Molecular mechanisms of the action of magnesium orotate on cardiovascular physiology // Cardiology. 2008. № 5. C. 65-7. 6. Shkolnikova MA Magnesium metabolism and the therapeutic value of its preparations. М., 2002. C. 28. 7. Shkolnikova MA, Erastova EK, Kleimenova NI, et al. The use of the drug Magnerot in the practice of pediatric cardiology // Difficult Patient. 2010. C. 1-2. 8. Ito N, Fukumoto S. Symptoms and management of tetany. Clin Calcium 2007;17(8):1234. 9. Pepe S, Leong J, Van der Merwe J, et al. Targeting oxidative stress in surgery: effects of aging and therapy. Exp Gerontol 2008;43(7):653-57. 10. Stepura O, Martynow A. Magnesium orotate in severe congestive heart failure (MACH). international J Cardiol 2009;131(2):293-95. 11. Thiel R. Can calcium metabolism disorders cause or contribute to myoclonic seizures in epileptics? Med Hypotheses 2006;66(5):969-74. 12. Gromova OA, Kudrin AV Neurochemistry of macro- and micronutrients. М., 2001. C. 300. 13. Wijst van der J, Joost G, Bindels RJM, et al. Epithelial Mg2+ channel TRPM6: insight into the molecular regulation. Magnesium Research 2009;22(3):127-32. 14) Li Y. Magnesium status and dietary intake of middle-aged people in a rural area in China. Magnesium Research 2009;22(2):66-71. 15) Ariza AS, Bobadilla N, Diaz L, Avila1 E, et al. Placental gene expression of calcitonin-generated peptide and nitric oxide synthases in preeclampsia: effects of magnesium sulfate. Magnesium Research 2009;22(1):44-9.15. C. Supakatisant and V. Phupong. Oral magnesium for the relief of pregnancy-related leg cramps: a randomized controlled trial. Maternal and Child Nutrition (2015), 11, p. 139.
muscle cramps and magnesium
convulsions
Convulsions are involuntary muscle contractions that vary greatly in duration, intensity and location, etiology and pathogenesis.
Mineral imbalances, particularly hypomagnesemia [1-11], contribute to the development of seizures. The contribution of magnesium to neuromuscular function has been convincingly demonstrated by evidence-based medicine and epidemiological studies [6, 13-15].
Myoclonus is a group of pathologies involving muscle spasms in the calves and hips. These spasms are caused by abnormalities in the neuromuscular apparatus.
The calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle) is located on the back of the lower leg. This muscle is connected to the heel bone via the Achilles tendon. The function of these muscles is to keep the body balanced when walking and running and to be able to move the feet.
The calf muscle is the most stretchable muscle.
Calf cramps are the most painful and are caused by strong involuntary tension in the calf muscle fibers.
The spasm is accompanied by acute pain syndrome, since several nerve endings in the lower limb are pinched at once.
Experts attribute night cramps to the slowing down of blood circulation, which cannot supply the organs and tissues with the required amount of nutrients.
Cramps in the calf muscles can be caused by the following processes.
- Heavy strain on the muscles. The calves are involved in all types of human physical activity: swimming, running, tennis, skating, squatting. Prolonged exertion can cause cramps.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Potassium and magnesium deficiencies often cause nighttime leg cramps. This cause is the most common problem in diagnosing cramps in pregnant women.
- dehydration. Cramps in the calf muscles are caused by excessive sweating and loss of fluids. During intensive exercise, important nutrients are flushed out of the body with sweat.
- Damage to the calf muscle. Unusual stress can lead to acute, persistent pain in the legs. In such cases, there is a suspicion of a strain or strain on the muscle. A doctor should be consulted for a correct diagnosis.
- Wearing poor quality shoes. Prolonged wearing of uncomfortable and tight shoes made of artificial materials causes cramps. If a woman wears high-heeled shoes that force the foot and lower leg to bend unnaturally, the risk of orthopedic problems increases.
- hypothermia. Seizures often occur after a bath in cold water or after prolonged exposure to the cold. The cold causes the vein and artery walls to constrict, slowing down cell metabolism.
prevention
Many injuries can be avoided if you follow a few simple rules. This includes:
- At least a light warm-up should be carried out before any physical activity.
- If you exercise, you should do it regularly.
- Do not start with a maximum load immediately. Start with a light load and increase it gradually.
- The shoes should be comfortable.
- Women should occasionally wear high heels to exercise the calf muscles.
- If you feel tired legs, you should always take a break.
Many sprains can be avoided by following these principles. In addition to preventive measures, it is also important to know how to treat injuries properly. The ankle is the most commonly injured part of the body. Information on first aid for sprained ankles can be found here.
First aid measures for a calf sprain
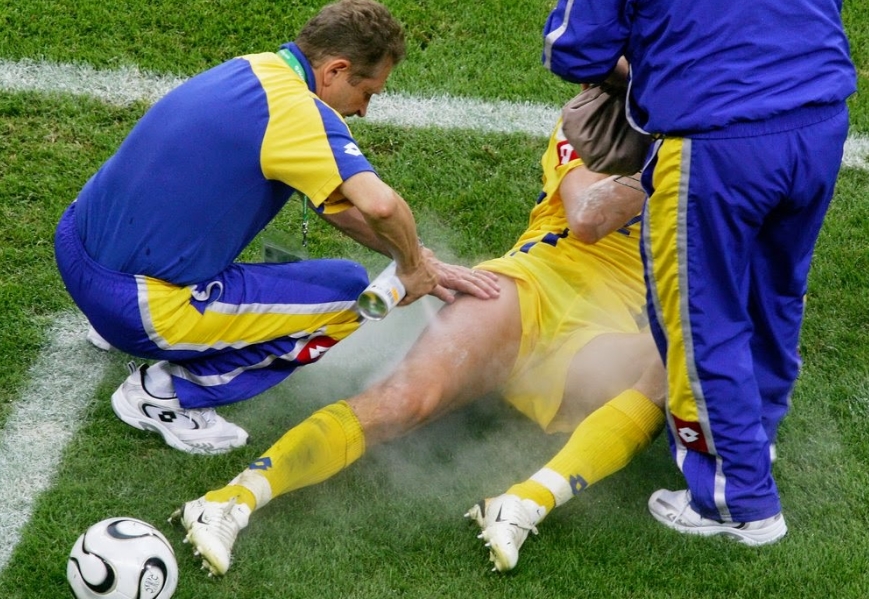

First, you should immobilize the patient. Be sure to put ice or something cool on the bruised area. Athletes use special freezing sprays in such cases. If the injury is severe, the person may even lose consciousness, so they should be positioned as safely as possible.
If the injury is minor, treatment can be done at home. If the pain is severe and acute, the victim should be taken to a trauma center for an accurate diagnosis. A muscle tear may require urgent surgery. The sooner this happens, the less time it will take for full recovery. This is because muscles that have long been torn are difficult to straighten and stretch when they have stitches.
Prevention of muscle cramps
Measures to prevent cramps include the following:
Muscle stretching exercises while running are most effective. Lunge: One leg is extended forward and bent at the knee, the other is behind and straight. You can brace yourself against a wall with your hands to keep your balance. Both heels are on the floor. Bend the front leg at the knee until you feel the muscles on the back of the other leg tighten. The greater the distance between your feet and the more the front leg is bent at the knee, the more the muscles are stretched. The muscles are stretched for 30 seconds and the exercise is repeated 5 times. The stretch series is then performed with the other leg.
Most medications commonly prescribed to prevent seizures (e.g., calcium supplements, quinine, magnesium, benzodiazepines) are not recommended. In most cases, these drugs are ineffective. Quinine has been shown to be effective in some studies but is generally no longer recommended due to episodic serious adverse reactions (e.g. cardiac arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [TTP] and hemolytic uremic syndrome [HUS], severe allergic reactions). Mexiletine may be useful in some cases, but the risk of worsening this drug's side effects remains unclear. These side effects include nausea, vomiting, heartburn, dizziness, and tremors.
Some athletic trainers and doctors recommend using saline for muscle spasms, but there is little data on its effectiveness.
Epileptical attack
An epileptic seizure, or status epilepticus as it is also known, is perhaps the clearest example of what the layperson imagines when speaking of seizures.
The person suddenly collapses, their body shrinks chaotically, there are incoherent breathing sounds, and they are foaming at the mouth. The picture is frightening and the situation requires urgent medical intervention. Surprisingly, a single intravenous injection quickly brings the person back to life.
What should I do? The main task of witnessing an epileptic state is to ensure the safety of the unfortunate person so that he does not accidentally injure himself on surrounding objects. If possible, the person should be placed on a soft surface and the head turned to one side to prevent vomit and foam from entering the respiratory tract. Medical emergency services should be called as soon as possible.
When a seizure first occurs, it is important to get a comprehensive evaluation as quickly as possible. It may be the beginning of a neurological disease or a brain tumor.
Application in children
Midocalm can also be used in children aged three and over, but only in a dosage of 50 mg tablets.

Adolescents aged 14 and over take the medicine like adults.
Injections are not recommended for minors.

Mydocalm analogues
- Sirdalud – this drug has a less broad spectrum but fewer side effects.
- Tolperizone – this drug is absolutely identical to 'Midocalum' and has the same active ingredient. Cheaper equivalent.
- Myolgin is prescribed for the same indications as Midocalm. Thanks to the paracetamol in the formulation, the drug also has an antipyretic effect.
- Baclofen – has similar effectiveness to Midocalm, but has a long list of side effects.
- Calmirex – has the same indications as Midocalm. Unlike Midocalm, there are no extended-release tablets in the product line.
Although the Midocalm analogues have the same properties, switching from one drug to another should only be done in consultation with your doctor.
specific treatment
The choice of treatment plan for calf pain depends on the cause of the discomfort. In most cases, surgery is not necessary, and conservative measures such as medications, physical therapy, and physical therapy may be sufficient. These measures contribute to:
- to improve blood circulation;
- to suppress inflammatory processes;
- eliminate pain and swelling;
- flush out toxins;
- Strengthening of ligaments and muscles.
It is dangerous to self-administer drugs and other therapeutic agents. For example, heparin-based drugs are prescribed for thrombosis, but if blood clotting is inadequate or the vascular walls are weakened, these preparations can cause bleeding. Excessive exercise can damage the musculoskeletal system, while insufficient exercise does not have the desired therapeutic effect. For this reason, only the doctor should draw up a treatment plan that includes a series of exercises.
The network of Hello! clinics has the most modern diagnostic equipment that enables an accurate diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. Experienced doctors develop individual treatment and rehabilitation plans for patients based on classic and modern techniques that allow them to get rid of their pain quickly and without side effects or the risk of relapse.
Causes of calf pain after running
Leg pain can have a variety of causes. Let's take a closer look at some of them.
Wrong technique

Running puts a lot of strain on our legs. As a result, the muscles do not get the substances they need and lactic acid forms.
To avoid calf pain, you need to make your upper body the trigger of the movement: lift the body as you inhale, draw in your stomach, relax your legs and move them as if they were suspended like your arms. Then, if you do everything right, you'll feel like your leg muscles aren't involved in the run.
You will not be able to avoid undue tension in your legs when running on an uneven track. In this case, you should use your hips and pelvis more actively - it should move like a rower's oars. This technique helps relieve stress on the calf muscles.
Poor quality of shoes

Uncomfortable shoes prevent feet from properly touching the ground and from properly distributing the load on the muscles. This also puts strain on the Achilles tendon, and the calves tire as a result.
Shoes must be selected correctly. They must be of good quality and include running shoes with insoles.
Sudden interruptions in exercise
When you run a certain distance, you should never stop abruptly. Switch to a slower pace, walk part of the way. Once you finish a run, you shouldn't stop immediately. Keep moving until your heart rate returns to normal.
specificity in girls

Diagnosis of calf pain

Your doctor will help you make the correct diagnosis and tell you that tests and x-rays should be taken for a comprehensive examination.
Calf pain after running can be the result of a metabolic disorder or various joint or spine problems.
After the examination, your doctor will give you the necessary recommendations.
prevention
Since the most common cause of lower limb ischemia is atherosclerosis, all preventive measures are aimed at preventing it. For this purpose it is recommended to:
- giving up unhealthy habits;
- adjust your diet;
- reduce and control body weight;
- increase physical activity;
- monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases.
At the first signs of lower limb ischemia, it is important to immediately seek medical attention and initiate appropriate treatment.
Popular Questions
In stage 1, there are no subjective symptoms that the patient can perceive. There are only objective symptoms: systolic murmur over the arteries of the lower limbs, weak pulsation. During this phase, exercise determines that the permeability of the arteries is impaired. Prolonged walking or running (several kilometers) causes pain in the leg, which does not receive adequate blood flow. They subside completely after a short rest. The pain is due to the clogged blood vessels not being able to carry as much blood as is needed to oxygenate the working muscles.
- Obesity;
- High blood pressure;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
- consumption of large amounts of animal products;
- low fiber intake;
- low physical activity;
- Smoke.
Chronic lower limb ischemia is treated conservatively. Drugs are prescribed to improve tissue trophism, expand vessels, prevent the formation of thrombi and normalize the rheological properties of blood. Blood pressure and lipid profile are normalized. Physiotherapeutic treatments, intravenous laser blood irradiation, therapeutic exercises, contrast agent treatments and hyperbaric oxygenation are used. In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed.
Read more:- Calf muscle cramps when walking.
- Why do your calves hurt when you run?.
- Calf pain after running.
- muscle work while running.
- Which muscles hurt after running?.
- Muscles congest when running.
- The calf is constipated when running.
- Lamb Muscle Soreness.
